Science:Math Exam Resources/Courses/MATH152/April 2016/Question A 25
{{#incat:MER QGQ flag|{{#incat:MER QGH flag|{{#incat:MER QGS flag|}}}}}}
• QA 1 • QA 2 • QA 3 • QA 4 • QA 5 • QA 6 • QA 7 • QA 8 • QA 9 • QA 10 • QA 11 • QA 12 • QA 13 • QA 14 • QA 15 • QA 16 • QA 17 • QA 18 • QA 19 • QA 20 • QA 21 • QA 22 • QA 23 • QA 24 • QA 25 • QA 26 • QA 27 • QA 28 • QA 29 • QA 30 • QB 1(a) • QB 1(b) • QB 1(c) • QB 1(d) • QB 2(a) • QB 2(b) • QB 2(c) • QB 2(d) • QB 3(a) • QB 3(b) • QB 3(c) • QB 4(a) • QB 4(b) • QB 4(c) • QB 4(d) • QB 5(a) • QB 5(b) • QB 5(c) • QB 5(d) • QB 6(a) • QB 6(b) • QB 6(c) •
Question A 25 |
|---|
|
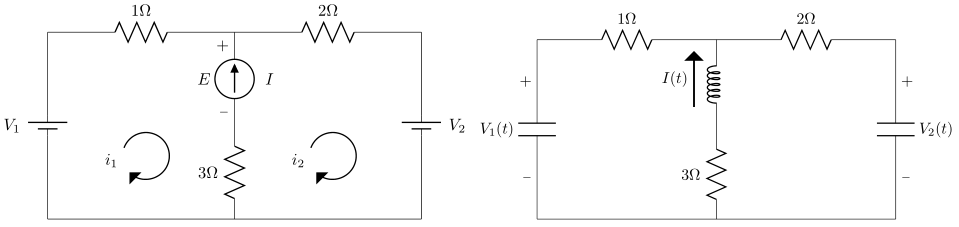
Questions A25 and A26 concern the circuits above. In the left diagram, is the current through the current source and is the voltage across it, to be determined. A25: For the left circuit above with two voltage sources and one current source write the one linear equation that matches the loop currents to the current source. |
|
Make sure you understand the problem fully: What is the question asking you to do? Are there specific conditions or constraints that you should take note of? How will you know if your answer is correct from your work only? Can you rephrase the question in your own words in a way that makes sense to you? |
|
If you are stuck, check the hint below. Consider it for a while. Does it give you a new idea on how to approach the problem? If so, try it! |
Hint |
|---|
|
Recall from Kirchhoff’s Laws that for any node, current in equals current out for any node, current in equals current out. |
|
Checking a solution serves two purposes: helping you if, after having used the hint, you still are stuck on the problem; or if you have solved the problem and would like to check your work.
|
Solution |
|---|
|
We follow the hint and apply Kirchoff's current law to the top node. The current coming into the node from the left is is , the current entering the node from the bottom is , and the current leaving the node from the right is . We therefore have . Solving for gives . Answer: |
{{#incat:MER CT flag||
}}