Course:MATH103/Archive/2010-2011/207/Lectures/Lecture03
| Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics | |
|---|---|

| |
| Course Pages | |
| Course Policies | |
| Math Solvers | |
| Exams | |
| Quizzes | |
| Assignments | |
| Lectures | |
Lecture 3
Readings For This Lecture
Keshet Course Notes:
Summary
1. Quiz dealing with sums (convergent and divergent solutions)
2. Discussion of assigned readings
3. Continued examples of summation notation and introduction to finite geometric series. A geometric series is one where all terms have the form , where is a real number and is an integer power.
.
4. Group exercise: Estimating the area of an abstract shape using squares and circles
Each group was asked estimate the area of their group's unique shape using 1) squares of like area and 2) circles of like area. Each group was asked which estimate was more accurate.
5. Calculate (sigma from k=1 to N=10)of (k+3)^2
Solution
foil and split the polynomial and use the summation formula to get (10(11)(21)/6) +(3(10)(11)/2)+90=805
Exercises
1. A finite geometric series with terms is a series of the form . The sum of such a series is provided .
The formula does not work if . Find the actual value of the sum for the case . Compute the sum of the series .
2. Find the sum of the first 11 numbers of the form . The sum of the first 21 numbers? The first 31 numbers? Can you see a pattern emerging?
| Solution |
|---|
| The sum of the first 11 such numbers is given by the geometric sum
approximately. The sum of the first 21 numbers is given by approximately. The sum of the first 31 numbers is given by approximately. This series is growing rapidly, almost tripling in size at each addition of 10 numbers. |
3. Find the sum of the first 11 numbers of the form . The sum of the first 21 numbers? The first 31 numbers? Can you see a pattern emerging?
4. Comment on the different patterns between the solutions to questions 2 and 3. Can you explain why they are different? Which pattern will stay finite if we continue to sum more numbers?
5. A branching colony of fungus starts as a single spore with a single segment of filament growing out of it. This will be called generation 0. The tip of the filament branches, producing two new segments. Each tip then branches again and the process repeats. Suppose there have been 10 such branching events. How many tips will there be? If each segment is the same length (1 unit), what will be the total length of all the segments combined after 10 branching events? (Include the length of the initial single segment in your answer.)
6. A plant grows by branching, starting with one segment of length (in the 0’th generation). Every parent branch has exactly two daughter branches. The length of each daughter branch is (2/5) times the length of the parent branch. Find the total length of just the 12’th generation branch segments. Find the total length of the whole structure including the original segment and all 12 successive generations. Find the approximate total length of all segments in the whole structure if the plant keeps on branching forever. (Your answers will be in terms of .)
| Solution |
|---|
| The length of the first generation branch will be . The second generation will have a length of . Continuing this pattern, the length of the 12th generation will be .
Since each branch creates 2 daughter branches, we have that after one generation there are branches. After the second generation, we have branches. Keeping with this pattern, we get branches at the 12th generation. Therefore, the length of all the 12th generation segments is given by approximately. The length of the entire structure up to the 12th generation is approximately. This is using our geometric series formula. If we let the structure branch on forever, the total length would be . |
7. Find the area of a regular octagon (a polygon that has eight equal sides). Assume that the length of each side is 1 cm. What is the area of the smallest circle that can be drawn around this octagon?
| Solution |
|---|
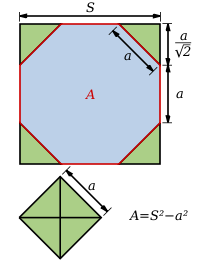 . Alternatively, we can divide the octagon into 8 isosceles triangles, as shown here [[1]], with base length of 1 and top angle of 45 degrees. At this point we can use the formula given in the course-notes about the area of an -gon. (pg 4)
(the last step can also be shown numerically with a calculator.) To find the area of the smallest circle that contains this octagon, we need only find the side length of the isosceles triangles found in the previous step. This would give the radius of the desired circle. We know the height of the isosceles triangle to be . Using this, we create a right angle triangle with this height, and base 1/2, which tells us the side length of the isosceles triangle must be
The area of the circle we are looking for is . |
8. Consider the function on the interval . Sub-divide this interval into 4 equal strips and use these strips to approximate the area under the function. First, use left-endpoints to determine the height of each strip when approximating the area. Then, use right-endpoints. Explain why these two answers are different.
| Solution |
|---|
| Using left endpoints, this area can be turned into the Riemann sum
approximately. In general, the formula for the left endpoints would be
The right endpoints would provide the Riemann sum approximately. The general formula would be . Note the similarities between the two methods. Only the indexing has appreciably changed. The actual area under this curve is approximately 1.7183. The right endpoints give an overestimate since these approximating rectangles would completely enclose the area. The left endpoints provide an underestimate since these rectangles all sit inside the area under question. |
9. Find the area between the -axis and the graph of between and . Do this by using the geometry of this region. Then, compute the area by finding a summation formula for the area of approximating strips, and letting go to infinity.