Course:FNH200/Projects/2020/Lay's Classic Chips
Introduction

History
Herman W. Lay introduced Lay's Chips in 1932, where he began his business in Nashville, Tennessee[1]. Lay started his small business selling his "Lay's Chips" from the trunk of his car to several grocers along the Southern States of America, in which he later became well known in various areas[2]. Lay's Chips was the first snack company to achieve commercial advertisements on television, and the successful Lay's Chip brand production began its incline in 1938. The national brand gained several Canadian consumers in 1962, and was popularized all around the world.
Two national marketing brand competitors, The Frito Company and H.W Lay's Company merged to form the "Frito-Lay" incorporated in 1961. The crispy, light textures contained in Lay's Classic chips became an efficient, simple snack to bring on any occasion.
Ingredients

- Russet Potatoes
- Vegetable Oil
- Salt
Processing
1. Peeling
The potatoes are collected from various farming plantations and transported to factories to undergo manufacturing. They are placed through a machine that automatically peels the exterior, where the results aim to provide accuracy and precision to ensure its quality is attained for the next steps of preparation[3].
2. Slice Washing

The primary function of a slice washer is to remove the starch from the potatoes. The nutrients of the potato slices are slowly lost as they continue through the processing steps. As they are being sliced, the machine washes each slice with a water solution containing potassium aluminum sulfate. This solution sterilizes each slice, as well as whitens the exterior surface[3]. After it has been sliced and cleansed, they are placed onto a conveyor belt that is beneath two hot air vents that remove the water from the surface of each chip slice.
3. Deep Frying
After the potato slices have been cleaned and surface dried by the hot air vents, they are placed into the deep frying cooker that contains hot oil at a temperature between 176.6°C-190.5°C. The thickness of each slice should be consistent, and have approximately the same amount of cooking time. The potato slice becomes a potato chip once it has completely been fried, dried and retains a crispy texture and refined golden brown color[4].
Excess oil is removed and filtered out from the deep frying machine, to produce potato chips with a minimal oil coating on the exterior surface.
4. Salting
When all potato chips have been fried, they are placed onto a conveyor belt where salt is sprinkled on the chip's surface to enhance its flavouring. Lay's classic chips only contain salt as its primary flavor enhancement. However, Lay's company produces many different flavors which require various seasonings[5].
Once they have finished the salting process, they are then packaged and sealed into bags that are filled with nitrogen gas.
5. Rejected Potatoes
Exterior bruising, microbial, or insect infestations can cause having to throw away some potatoes. Quality control differentiates between the potatoes that can be processed to make chips and those that did not pass the test. Animal feed can be created out of the potatoes that have been rejected[6].
Preservation Methods
Deep Fat Frying
A dehydration method which evaporates nearly all the water content present in the commercially produced potato chips. The usage of hot oil at a temperature of 350-375°F (176.6-190.5°C) causes the tissue cells to shrink, increasing water evaporation and reducing its overall water activity[7].
Salt
The addition of salt found on the surface of the chips also lowers the product's water activity and prevents microbial growth spoilage while decreasing chemical reactions. Contributes to retaining the shape, texture, flavor and color of the product[8].
Antioxidants
In some fried foods, antioxidants are added into the food product to reduce the chances of rancidity[9].
Packaging & Safety Regulations

The entry of water vapor in the Lay’s Chips bags is prevented by filling the pack with dry gas[7]. Quality deterioration of the chips is inhibited by adding nitrogen gas into the bag[10]. Using nitrogen gas over oxygen gas aids in the freshness, texture, and color presentation of the product and prevents oxidative rancidity. As one may notice, when the bag is opened and exposed to oxygen for an extended period, the chips become stale, which is the cause for their deterioration in quality[11].
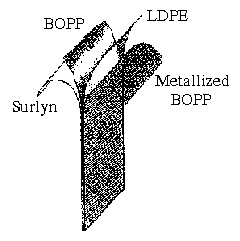
The package consists of four layers. A polymer material called Bi-axially Oriented Polypropylene (BOPP) is used for the innermost layer[12].BOPP material is covered by a Low-density Polyethylene (LDPE) for greater strength and resistance against the exterior surroundings[12]. Another layer of BOPP then follows this. Lay’s Chips then uses Surlyn on the outermost layer, which is made from thermoplastic resin. This material strengthens and serves as a protective barrier against penetration, sealed with the heat at low temperatures[12].
The Lay’s company follows Division 23 of the Food and Drug Act in Canada when packaging their products[13]. Additional regulatory rules are enforced for the food and packaging safety under Division 24, 25, and 28.
Any packaging material for products produced after 2014 needs to be registered on the Government of Canada website and is closely monitored by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA). Manufacturers do not need to pre-register but need to double-check the accuracy of the list as it was updated in 2016[14].
Storage & Shelf Life
Storage
In order to maintain the quality of potato chips, several methods and surrounding conditions should be considered. The best places to store bags of potato chips are in dry areas that have cooler temperatures. Ensure the packaging that holds the potato chips are completely sealed from exposure to atmospheric air, such as using an airtight container or removing as much excess air from the package itself[15]. The freezer is another storage method that can be used in areas that are more humid than others[16]. It provides both a cool and dry environment that is suitable for potato chips and doesn’t cause the thawing of chips to occur. Check to make sure there are no tears in the package's exterior that will allow entry of air.
What containers or material can be used to seal chips at home?
- Use a Ziploc bag and seal out all air completely
- Use clips, paper clips, or clothespins to close the packaging of the chip bag
- Roll the packaged chip bag completely, and seal out air
Shelf Life
The shelf life of a food item describes the time to which an item can maintain its quality[17]. It can be extended by proper packaging and storage. Chips are considered semi-perishable food, a food product that does not need to be refrigerated but still has a limited time before it loses its peak quality[17]. Lay's Classic Chips have a shelf life of 26 weeks, approximately six months[18].
When the shelf life has passed, it means the food is no longer at its peak quality[19]. It is still safe to consume, unlike the expiration date (or Best Before), by which the product is no longer safe to eat[19]. It is also worth noting that different flavors produced by the Lay's company have varying shelf lives.
Effects On Health
Negative Effects
Lay's Classic chips are among the most popular and well-known snacks that are sold all around the world. Despite its rise in demand, these snacks have limited nutritional benefits due to processing that removes most of its beneficial nutrients. A regular diet containing eating chips or similar deep-fried products can affect your health and lead to potential weight gain if consumed frequently[20].
a) Sodium Content
The primary flavoring agent of Lay's Classic chips is salt. As Lay's Chips produce a variety of different flavours, most of their chip products are comprised of high sodium levels. Consuming high amounts of sodium can affect arterial blood pressure and can induce heart and kidney disease[21].
b) Oil / Fat Content
Deep frying is an efficient cooking method that requires less time while producing flavorful and crispy food products. Regularly eating deep-fried chips is associated with cardiovascular diseases producing symptoms related to shortness of breath, chest pain and numbness in various areas. Fatty plaque can accumulate along the blood vessel interior causing the heart to use more force to aid in blood circulation; this contributes to elevated blood pressure levels[22].
c) Acrylamide
Acrylamide is a substance created when food products are produced at high temperatures, where a chemical reaction between asparagine and sugar come into contact. Potatoes are carbohydrates that have starch, and starch contains glucose. The glucose molecules will interact with asparagine, an amino acid that is present in potatoes. Acrylamide is formed after the deep-frying process is finished. The dietary health risks when consuming acrylamide can result in cancer. Be aware that the darker appearance of a potato chip equates to a higher concentration of acrylamide[23].
Potential Benefits
One may also wonder why chips are very addictive. A significant amount of potato chips have high salt and fat content. Studies have proven that consuming salt can cause dopamine release[24]. This chemical messenger control’s the pleasure center of the brain. Dopamine is also known as the “happy hormone”, and when it’s first triggered it will then crave for more.
Potato chips are known not to be healthy. However, they do have some positive aspects. Lay's Classic Potato Chips do not contain any preservatives or additives. 1 oz serving of these chips is shown to have no cholesterol. In 1 oz, it also contains 1 gram of fibre, 9% of potassium, and 10% of vitamin C content. Polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats are known to be the healthier fat substitutes used for Lay's Classic chip production. An amount of 6% saturated fat is present in 1 oz of Lays Chips, and no trans fat (those which contain Low-Density Lipoproteins) is used during processing[18]. It is recommended to eat chips as little as possible, or at least eat in moderation to avoid detrimental health risks.
Potential Exam Question
Question:
Lay’s Classic Chips are produced by _________. If these chips are exposed to oxygen, oxidative _________ occurs. Therefore, when buying Lay’s Chips, _________ gas is filled inside the chip bag to retain its physical textures, characteristics and quality.
Answers:
- Oven Baking; Deterioration; Oxygen
- Pan Frying; Retrogradation; Carbon Dioxide
- Deep Fat Frying; Rancidity; Nitrogen
- Sun Drying; Gelatinization; Carbon Monoxide
Why the Question should be on the Final Exam:
The Material covered in this question is taught in “Lesson 5: Rational For Food Preservation” and holds significance towards the methods of processing and packaging of chips that many of us buy and consume from various stores.
References
- ↑ "Lays Canada". 2020.
- ↑ Attride, Tiana (2020). "10 things you probably didn't know about Lay's potato chips". Insider.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Goyal, Bhupesh (2018). "Manufacturing of Potato Chips and its Quality Improvement" (PDF). Journal of Food: Processing & Technology. 9: 9–12.
- ↑ Chan, Judy (2020). "Dehydration as a food preservation method". FNH 200.
- ↑ "How Frito-Lay makes potato chips". YouTube. 2011.
- ↑ "How Frito-Lay makes potato chips". YouTube. 2011.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Chan, Judy (2020). "Dehydration as a Food Preservation Method". FNH 200.
- ↑ Henney, Jane; Taylor, Christine; Boon, Caitlin. (2010). Strategies to Reduce Sodium Intake in the United States. United States: National Academies Press. pp. 91–92. ISBN 0-309-14805-7.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ Henney, Jane; Taylor, Christine; Boon, Cailtin. (2010). Strategies to reduce sodium intake in the United States. United States: National Academies Press. p. 113. ISBN 0-309-14805-7.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ "WHY ARE POTATO CHIP BAGS FILLED WITH AIR? USING NITROGEN IN POTATO CHIP BAGS".
- ↑ "How do potato chips stay so fresh in the bag?". PureAire Monitoring Systems. 2018.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "The Incredible Process of Packaging Potato Chips".
- ↑ "Packaging Materials". Government of Canada. 2020.
- ↑ "Reference Listing of Accepted Construction Materials, Packaging Materials and Non-Food Chemical Products Database". Government of Canada. 2017.
- ↑ "Keeping Chips Fresh – The Ultimate Guide". Foodsguy. 2020.
- ↑ Stice, Joel (2019). "You've been storing potato chips wrong your entire life". Mashed.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Chan, Judy. "Factors Affecting Microbial Growth, Enzyme Activity and Chemical Reactions in Foods".
- ↑ "Dutch Food Delights".
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "FOOD STORAGE - HOW LONG CAN YOU KEEP...POTATO CHIPS, COMMERCIALLY PACKAGED - UNOPENED".
- ↑ Camila Lama, Siddhi. "Why Are Chips Bad for You?".
- ↑ Middleton, Andrea. "Are Lay's Potato Chips Bad For You?".
- ↑ Gadiraju, T.; Patel, Y.; Gaziano, M. & Djousse, L. (2015). "Fried Food Consumption and Cardiovascular Health: A Review of Current Evidence". Nutrients. 7: 8424–8430 – via ProQuest.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ↑ Watson, Stephanie (2017). "How Bad for You Are Fried Foods?". WebMD.
- ↑ Laliberte, Marissa (2018). "This Is Why You Can't Ever Just Eat One Potato Chip, According to Science". The Healthy.