Documentation:CHBE Exam Wiki/Module 3 - Separations 1
| CHBE 241 Exam resources wiki | |
|---|---|

| |
| Chemical and Biological Engineering | |
|
Welcome to the CHBE Exam Resources Wiki!
This wiki is intended to host past exams | |
| Past Exams | |
| Final Exam 2016W | |
| Midterm Exam 1 2016W | |
| Midterm Exam 2 2016W | |
| Problem Sets | |
| Module 1 - Process Basics | |
| Module 2 - Reactors | |
| Module 3 - Separations 1 | |
| Module 4 - Separations 2 | |
| Module 5 - Non-reactive Energy Balances | |
| Module 6 - Reactive Energy Balances | |
Question 1
Convert the temperatures in parts (a) and (b) and temperature intervals in parts (c) and (d):
a) T=95°F to °R, °C,K
b) T=-50°C to K, °F, °R
c) ΔT=50°C to K, °F, °R
d) ΔT=120°R to °F, °C,K
Question 2
To regulate the temperature of a sand bath, a thermostat control with dial markings from 0 to 100 is used. A straight line that passes through the points (30, 300°F) and (90, 660°F) represents a calibration plot on the logarithmic coordinates of temperature (°F) versus dial setting,D.
Question 2a
Determine the equation for T in terms of D
Determine the slope and intercept,
Hence,
Question 2b
What is the estimated dial setting to obtain 500°F?
Question 3
The following data was obtained from an experimental run,
| x | 0.5 | 1.4 | 11 | 35 | 54 | 72 | 84 |
| y | 2.1 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6 | 6.25 |
Question 3a
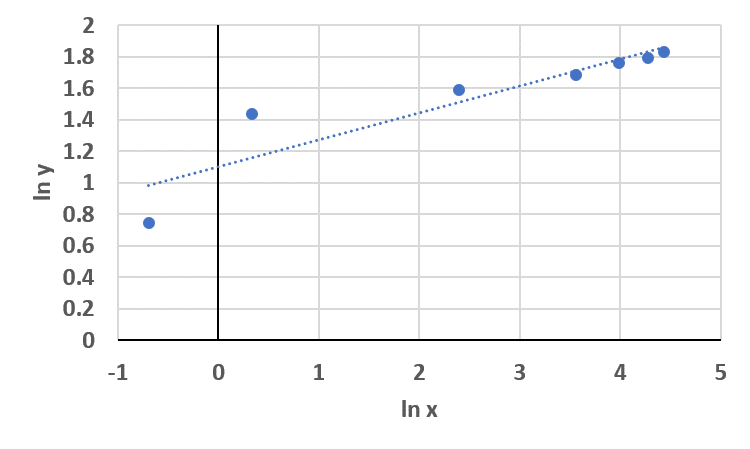
Plot the data on logarithmic axes
Question 3b
Determine the coefficients of power law expression y =axb
Question 4
Calculate the pressure and gas-phase composition (mole fraction) in a system containing a liquid that is 0.5mol% N2 and 99.5 mol% water that is in equilibrium with nitrogen gas and water vapor at 90°C
Use Henry's law for N2
At 90°C, HN2 is 12.6 × 104 atm/mol
The partial pressure of N2 is then
Use Raoult's law for water
At 90°C, pH2O* is 525.76 mm Hg [0.692 atm]
The partial pressure of H2O is then
The total pressure of the system is
The vapor mole fractions:
Question 5
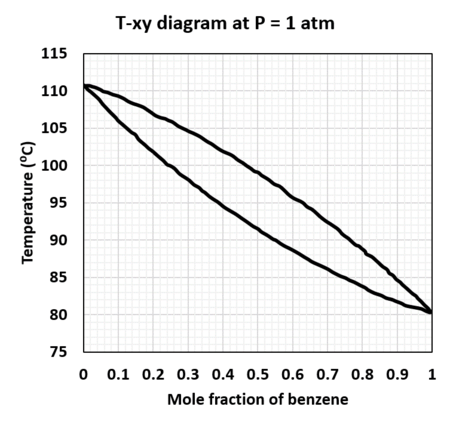
A mixture in the gaseous phase at 1 atm consisting of 40 mole% benzene and 60% toluene is cooled isobarically from an initial temperature of 115°C
Question 5a
At what temperature does the first drop of condensate form?What is its composition?
Hint: Find the intersection of the vapor curve with yB is 0.4
Question 5b
Determine the mole fractions of benzene in the vapor and liquid phases when the temperature of the system is at 98°C.
What is the ratio (total moles in vapor/total moles in liquid) at this point.
Hint: Find the intersection of the vapor and liquid curve when T is 98°C
Assume that the number of moles in the system is 1 mol.
Solving the 2 systems of equations,
Ratio of vapor to liquid: 0.75
Question 5c
At what temperature does the last bubble of vapor condense?What is its composition?
Hint: Find the intersection of the liquid curve with xB is 0.4
Question 6
A tank containing 50L of air-carbon tetrachloride gas mixture is at a temperature of 50°C, at an absolute pressure of 1.5 atm and a relative saturation of 40%.
To remove the CCl4 through gas adsorption, activated carbon is added to the tank. The volume of activated carbon can be assumed as negligible.
Question 6a
Calculate pCCl4 at the moment the tank is sealed, assuming ideal gas behavior and neglecting adsorption that occurs prior to sealing.
Let CCl4 be c
Question 6b
Calculate the total pressure in the tank and the partial pressure of carbon tetrachloride at a point when quarter of the CCl4 initially in the tank has been adsorbed.
Determine the initial moles of gas in the tank
Initial number of moles of CCl4 in the tank
Total number of moles of CCl4 adsorbed
Total number of moles in the tank
Pressure in the tank after adsorption [Assume T and V are constant]
Partial pressure of CCl4
Question 6c
How much activated carbon must be added to the tank to reduce the mole fraction of CCl4 in the gas to 0.001? Assume that the following relationship is true for the conditions in the tank
Determine the number of moles of air in the tank
Determine the number of moles of CCl4 in the tank
Determine the number of moles in the tank
Determine pc in the tank
Determine the mass ratio of adsorbed CCl4 to carbon in the tank
Determine the mass of CCl4 adsorbed
Determine the carbon required
Question 7
A solution containing 100 lb KNO3 /100 lb H2O is cooled in a cooling crystallizer operating at 30°C. The slurry of from the crystallizer contains solid crystals suspended in saturated solution which then fed to a filter to separate the solid and liquid components.
Question 7a
Determine the production rate of crystals (lb /lb feed).
At 30°C, the solubility of the salt in water is 48g KNO3 /100 lb H2O
Mass balance [using 1lb as basis for the feed solution]:
Let m1 be the mass of the saturated solution leaving the crystalizer in terms of the mass flow rate of the feed stream and
m2 be the mass of crystals in terms of the mass flow rate of the feed stream
Question 7b
Determine the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of the slurry leaving the crystallizer