Course:PostgradFamilyPractice/ExamPrep/99 Priority Topics/DVT
Deep Venous Thrombosis - Key Features
1. In patients complaining of leg pain and/or swelling, evaluate the likelihood of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) as investigation and treatment should differ according to the risk.
2. In patients with high probability for thrombotic disease (e.g., extensive leg clot, suspected pulmonary embolism) start anticoagulant therapy if tests will be delayed.
3. Identify patients likely to benefit from DVT prophylaxis.
4. Utilize investigations for DVT allowing for their limitations (e.g., Ultrasound and D-dimer).
5. In patients with established DVT use oral anticoagulation appropriately, (e.g., start promptly, watch for drug interactions, monitor lab values and adjust dose when appropriate, stop warfarin when appropriate,provide patient teaching).
6. Consider the possibility of an underlying coagulopathy in patients with DVT, especially when unexpected.
7. Use compression stockings in appropriate patients, to prevent and treat post-phlebitic syndrome.
Introduction
Risk factors= acronym THROMBOSIS
- Trauma,hypercoag.,OCP,malignancy,birth control,obesity,surgery,immobility,sickness
Most important sequale is venous insufficiency pulmonary embolism in 50%of proximal thrombosis
Etiology =Virchow’s triad
Endothelial injury, stasis & hypercoagulability
Hypercoag may be inherited or idiopathic & acquired like age(60), trauma, surgery, neoplasm, hyperhomocystinemia (TT folic acid 5mg daily), antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA), blood dyscriasis, hormones & immobilization
Clinical picture:
Homan’s sign is calf pain on dorsifection of the foot (classic sign but not specific or sensitive)
Tenderness of affected leg and palpable cord like structure are also classic symptoms
Unilateral leg edema is the most sensitive indicator of DVT
Differential Diagnosis
- Ruptured Baker’s cyst
- Cellulitis
- Ruptured Achilles tendon
- Lymphedema
- Superficial phlebitis
Algorithm for the Initial Work-up of Suspected DVT
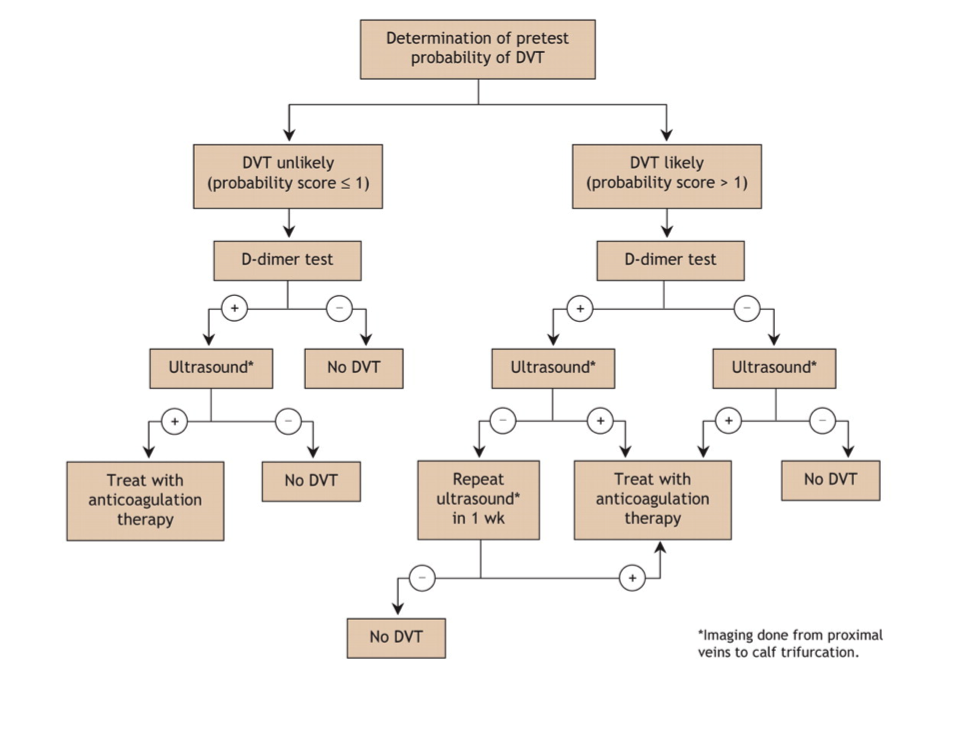
D-dimer (fibrin degradation product) is usually increased in thromboembolic disease
Sensitivity of about 80% for DVT but Specificity of 30% [i.e. not the greatest test]
Real utility is its negative predicative value of over 90% [useful only if the test is negative]
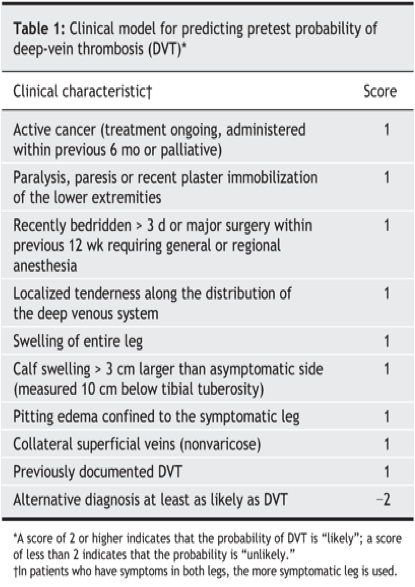
Many studies show that low pre-test probability by Wells criteria and negative d-dimer rules out DVT
- There is about 1% false negative rate with negative US and negative D-dimer
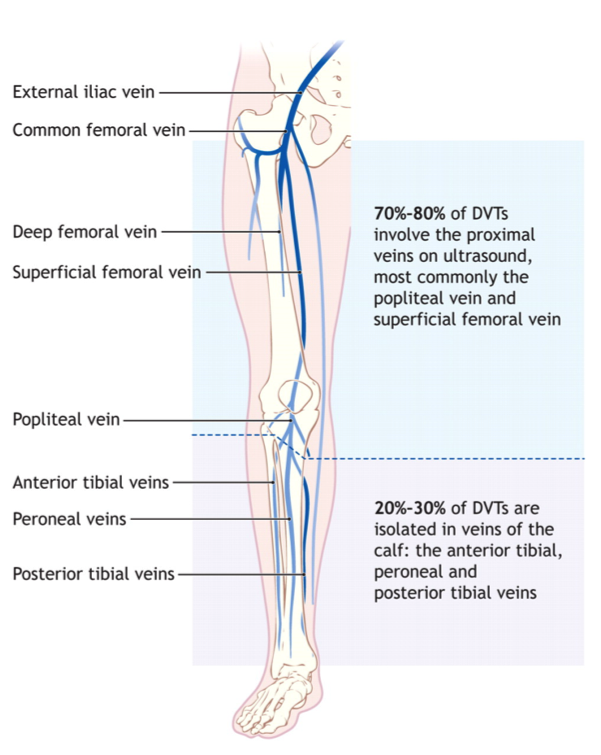
Doppler (95% sensitive for proximal DVT, 75% for distal calf DVT)
Distinction between proximal and distal DVT is important because calf only DVT rarely leads to PE
Prevention of pulmonary embolism is the reason for treating patients with DVT
Initial treatment
Unfractionated heparin =bolus 7500-10.000 IU followed by infusion of 1000-1500 IU\H or weight based monogram
- Reversible by protamine
- Need to monitor aPT(level=2xnormal)
LMWH: subcutaneous as effective as heparin
- No monitor
- Lower risk of HIT
- Renal clearance & need adjustment
HIT patients = need hirudin, fondaparinux
If life threatening thrombosis we can use thrombolytic drugs like TPA, streptokinase
Long term treatment
Warfarin with target INR
LMWH in cancer patients
- DVT 1st episode=duration 3 months
- 1st episode with ongoing risk like cancer, APLA consider indefinite period of treatment.
- 1st episode with single inherit risk 6-9 months or indefinite
- Recurrent DVT=indefinite period.
- IVC filters if anticoagulant contraindications, with recurrent PE, pulmonary HTN, or pt require urgent surgery.
- Pregnancy=use LMWH then warfarin 4-6 weeks postpartum. Total duration 3-6 M.
Initiation of warfarin
10 mg dose= shorter time to get target INR than start with 5mg without increase of side effects.
Overlap 4-5 days of heparin & warfarin required
Heparin antagonist vitamin K should be discontinued once harm stopped otherwise increase VTE.
Prophylaxis=BID 5000 IU if low risk, TID if high risk
- Risk of bleeding from heparin 7%
- Absolute contraindications of heparin: Include blood dyscrasias, recent ocular, intracranial surg., recent ICH, active bleeding
- DVT initial u\s should be followed by another u\s in a week to for extension to proximal veins