Course:FNH200/Assignments/2023/Smucker's Pure Strawberry vs No Sugar Added Jam
Introduction
Smucker's Pure Strawberry Jam and No Sugar Added Strawberry Spread
For over a century, Smucker's has been synonymous with high-quality fruit spreads. Established in 1897 by Jerome Monroe Smucker, Smucker's began as a small family business in Orrville, Ohio, and has withstood the test of longevity as it still remains a top competitor today[1]. This following will showcase the brands ability to retain its originality despite being offered in both the Smucker's Pure Strawberry Jam and the Smucker's No Sugar Added Strawberry Spread.
Product Visuals
Table 1. A comparison of Smucker's Pure Strawberry Jam and No Sugar Added Strawberry Spread jars, labels, and ingredient lists.
Ingredient lists
| Pure Strawberry Jam | No Sugar Added Jam |
|---|---|
|
|
| Pure Strawberry Jam | No Sugar Added Jam |
|---|---|
|
|
Role of Substitutes and Additives
Sugar Substitutes
- Sucralose: Sucralose is a synthetic sugar substitute that is created by replacing three hydroxyl groups of the sucrose molecule with chlorine.[2] It possesses a similar sweet taste to sucrose but is 600 times sweeter.[2] As such, it is an effective substitute for sucrose since similar or even greater sweetness levels can be achieved with significantly smaller dosages. For reference, one serving of Pure Strawberry Jam is composed of 66% sugar, while one serving of No Sugar Added Spread is composed of 0.047% sucralose and only 27% sugar from strawberries. Further, sucralose may be a beneficial sugar substitute for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to minimize carbohydrate and caloric intake as it is not metabolized by the body. Since it cannot be digested, it contributes zero energy and does not affect blood glucose or insulin levels.[2]
Thickeners/Emulsifiers
- Pectin and Guar Gum: Pectin and guar gum both act as thickening agents which help achieve a desired texture and gel-like structure.[3] No Sugar Added Spread is composed of more liquid (water and white grape juice concentrate). Thus, thickening agents are required to achieve a jam-esque consistency. Without thickeners, the jam would overall have an undesirable consistency and mouthfeel with poor spreadability. Guar gum acts as an emulsifier as it helps stabilize the texture of the jam by preventing separation. It allows for the jam to remain as a homogenous mixture with all ingredients suspended throughout. As such, it prevents separation and thus improves the appearance of the product.[4]
- Citric Acid: Citric acid is commonly regarded as a preserving agent, however, it also acts as an emulsifier as it has been shown to increase the viscosity of pectin emulsions.[5]
Preservatives
- Potassium sorbate: Potassium sorbate functions as a preservative since it is an antimicrobial agent which delays the onset of food spoilage as it suppresses growth of microorganisms. This prolongs product shelf life as it maintains freshness by preserving the flavour and texture of the jam. [6]
- Citric Acid: Citric acid is a naturally occurring antioxidant which lowers pH and thus has antimicrobial effects.[7]
Firming Agents
- Calcium Chloride: Calcium chloride functions to precipitate residual pectin.[8] The calcium ions activate pectin, augmenting gel formation and forming a firm gel structure.[8] Calcium chloride also prevents excessive softening and prolongs shelf life through maintenance of desired texture and colour.[9]
Colouring Agents
- Allura Red and Brilliant Blue FCF: Allura red and brilliant blue FCF are additives which function solely as colouring agents. As No Sugar Added Spread contains added water and concentrated white grape juice, it requires the use of additional colouring agents to avoid undesirable discolouration and achieve a traditional strawberry red colour.[10] As humans, we have a natural instinct to evaluate food quality based on their appearance, thus, an enhanced natural pigment is required to attract consumers. [10]
Comparison
Common Ingredients
The common ingredients between the two products are strawberries, citric acid, and pectin. Strawberries are used in both jams as the primary ingredient and foundation for the jam’s fruit flavour. Citric acid provides tartness and acidity[11] while pectin acts as a gelling agent, providing the gelatinous, thick consistency common to jams[12].
Differences
1. Sweeteners
- Pure Strawberry Jam contains regular sugar and glucose-fructose (high-fructose corn syrup), which contribute to a higher caloric content per gram of consumption.
- In No Sugar Added Spread, concentrated grape juice is used as a natural sweetener instead of regular sugar. Sucralose is also added as an artificial, non-caloric sweetener. The addition of sucralose preserves the sweetness typical of jams, but significantly reduces the caloric content as sucralose contributes zero calories per gram of consumption[13].
2. Colouring Agents
- Allura Red and Brilliant blue FCF are added to No Sugar Added Spread to enhance the appearance of the jam and to potentially restore the discolouration resulting from the variations in ingredients and processing methods compared to its regular counterpart.
3. Preservatives
- Potassium sorbate is added to No Sugar Added Spread as a means of preserving its shelf life and inhibiting the growth of mold and bacteria[14]. This ingredient is necessary for No Sugar Added Jam as it contains a much lower sugar concentration compared to regular jam. Regular jam, on the other hand, relies on its higher concentration of sugar to act as a preservation agent and inhibit the growth of undesirable microorganisms[15].
4. Other Textural Ingredients
- Water, guar gum, calcium chloride are also added to No Sugar Added Jam for firming, emulsification and textural purposes. Water is used in No Sugar Added Jam to activate the additives and to control the consistency of the jam.
- Since Regular Jam contains a high natural sugar content, the viscosity of the jam can be controlled more easily[16]. No Sugar Added Jam requires guar gum and calcium chloride to act as a firming agent and stabilizer to produce the same kind of consistency found in regular jam. Furthermore, since concentrated grape juice and water are added to No Sugar Added Jam, potentially diluting the mixture, these firming agents help to act as a thickening agent and improve the texture of the jam.
Description of Labels
| Requirement | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bilingual Labelling | Both labels contain bilingual labelling, with all text written in English and French, allowing both products to comply with regulatory requirements. For example, the pure strawberry jam is labelled as both "Strawberry Jam" and "Confiture de fraises". The text that states "no sugar added" on the no sugar added jam label also states "sans sucre ajouté", which is French for the same statement. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | While both products include the common name for the food, satisfying regulatory requirements, the pure strawberry option interestingly is called jam, while the sugar-free option is called spread. In fact, the sugar-free option is actually labelled as a "fruit and concentrated white grape juice spread", presumably to meet labelling requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Country of Origin | As both products are produced by Smucker's in Canada, there is no indication of the country of origin on either label, which meets regulatory requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Date Marking and Storage Instructions | It can be seen that the regular jam has instructions to refrigerate the product after opening. On both jams, a space for the best before date to be printed is also included. This satisfies the regulatory requirement that date and storage instructions are required. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Identity and Principal Place of Business | Both products include the address and phone number, as well as the name of the company producing the product, The Smuckers Company. This also satisfies regulatory requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Irradiated Foods | As both products are not irradiated, there is no indication of irradiation on either label, which meets regulatory requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Legibility and Location | The labels on both products are clearly legible, and located on the center of the jar which the products are contained in, making it easy to read and allowing it to fulfill this requirement. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| List of Ingredients | Both products include a list of ingredients on the labels. While our group cannot confirm that they are listed in descending order of proportion, they presumably are in order to meet regulatory requirements. | |||||||||||||||||||||
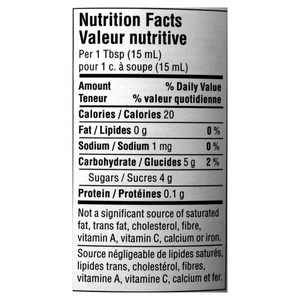
| Nutrition Facts Table | The nutrition facts table indeed shows the calories, amount of fat, sodium, carbohydrates, sugars, and protein in 1 tablespoon of each product respectively. In both cases, it is stated that the product is not a significant source of saturated fat, trans fat, cholesterol, fibre, calcium, iron, or vitamins A and C. The nutrition facts tables are as follows:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Quantity of Food | On both labels, the net quantity of the food is stated on the front, measured in milliliters, which satisfies regulatory requirements. The labels we used state a quantity of 500mL for the pure strawberry jam and 310mL for the no sugar added strawberry spread, although it should be noted that both products can come in other quantities as well. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sweeteners | The no sugar added jam states that it is sweetened with sucralose, satisfying the requirement that certain artificial sweeteners must be labeled in this fashion. The regular jam is sweetened using sugar (sucrose), so it does not have to explicitly state what it is sweetened with. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Claims and Statements | The regular jam claims that it has no artificial colours added, and the no sugar added jam claims that it has no sugar added. |
References
- ↑ "J. M. Smucker competitors and similar companies". Craft.co. Retrieved July 18th, 2023. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "FNH200 Lesson 4". UBC Wiki. Retrieved July 16, 2023.
- ↑ "Lesson 2". Retrieved July 17, 2023.
- ↑ "Guar gum: processing, properties and food applications—A Review". Journal of Food Science and Technology.
- ↑ Duan,, Xingke (October 2021). "Structural and Emulsifying Properties of Citric Acid Extracted Satsuma Mandarin Peel Pectin". Foods. 10 – via Pubmed.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetic and toxicological aspects of potassium sorbate food additive and its constituents". Trends in Food Science and Technology: 123–130.
- ↑ Soloft-Jensen, Jakob (May 2007). "New Chemical and Biochemical Hurdles". Emerging Technologies for Food Processing: 387–416 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Pectins - Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications. 2020. ISBN 978-1-78984-072-8.
- ↑ "What is Calcium Chloride (E509) in food and its common uses?".
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Natural Food Colorants and Preservatives: A Review, a Demand, and a Challenge". Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry.
- ↑ Poerwono, Hadi; Britain, Harry G. "Citric Acid".
- ↑ Flutto, L. "Pectin".
- ↑ Chan, Judy C. K. "FNH 200: 3.1.2 Types of Sugar Substitutes - Sweeteners".
- ↑ Morris, William C. "Low or No Sugar in Jams, Jellies and Preserves" (PDF).
- ↑ Chan, Judy C. K. "FNH 200: 2.2.1.1 Carbohydrates".
- ↑ Chan, Judy C. K. "FNH 200: Functional Properties of Simple Sugars in Foods".
| This Food Science resource was created by Course:FNH200. |