Course:FNH200/Assignments/2020/Kraft Miracle Whip
Introduction
Miracle Whip is a condiment manufactured by Kraft Foods in 1933 as a less expensive alternative to mayonnaise[1]. Mayonnaise is a condiment frequently used in households and restaurants. It is used as a base for sauces, in sandwiches and many more. Known to consist mostly of oil, mayonnaise may be viewed as an unhealthy sauce and potentially healthier alternatives of mayonnaise can be explored. Miracle Whip cannot even be considered as mayonnaise as it contains less than 65% vegetable oil.[2] Miracle Whip is therefore considered a spread, which contains less fat and calories than mayonnaise, and has alternatives available. We would like to compare the original, calorie wise and fat-free choices.
Pictures




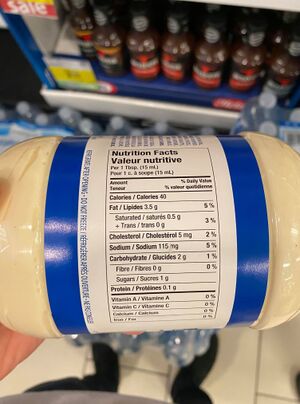





Ingredient Lists
| Miracle Whip Original Spread | Miracle Whip calorie-Wise Spread | Miracle Whip Fat-Free Spread |
|---|---|---|
| water, soybean oil, sugar/glucose-fructose, vinegar, modified cornstarch, egg yolks, salt, mustard, spices, potassium sorbate (maintains quality), calcium disodium EDTA, dried garlic. | water, soybean oil, glucose-fructose, vinegar, sugar, modified cornstarch, salt, whole eggs, egg yolks, corn dextrin, mustard, microcrystalline cellulose, spices, potassium sorbate, xanthan gum, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, calcium disodium EDTA, dried garlic | water, sugar, vinegar, modified cornstarch, soybean oil, salt, corn dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose, egg yolks, citric acid, xanthan gum, colour, potassium sorbate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, mustard, lactic acid, spices, calcium disodium EDTA, sodium aluminum silicate,dried garlic |
| Fat Substitutes[3] | Sugar Substitutes[4] | Additives[5] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miracle Whip Original Spread |
|
none |
|
| Miracle Whip calorie-Wise Spread |
|
none |
|
| Miracle Whip Fat-Free Spread |
|
none |
|
Roles of Fat Substitutes, Sugar Substitutes and Additives
Fat Substitutes:
Fat substitutes are materials that simulate the chemical and physical properties of fats used to replace fat in high fat foods. These carbohydrate based fat substitutes (corn dextrin, xanthan gum, modified cornstarch, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium carboxymethylcellulose) are used to thicken, flavour, and smoothen the texture of the product to provide a fat mouthfeel while contributing to fewer calories.[3]
Sugar Substitutes:
Sugar substitutes are materials that simulate the chemical and physical properties of sugars. Sugar substitutes can be used for weight loss, preventing dental decay and helps to control blood sugar in those with diabetes. Sugar substitutes add a sweet taste to food. Sugar substitutes were not used in these products. [6]
Additive:
An additive is a substance which affects the characteristics of a food when used.[5]
- Types of additives[7]:
- Anticaking agent: Additive that prevents lump formation in powders and allow them to move freely (eg. sodium aluminum silicate)
- pH adjusting agents, acid reacting materials and water correcting agents: Adjusts the pH of food to maintain acidity or alkalinity (eg. lactic acid)
- Preservative: Slows down the onset of food spoilage by inhibiting the growth of bacteria (eg. potassium sorbate and citric acid)
- Sequestering agent: An agent that binds to undesirable metal ions in foods that may cause color, flavour or textural changes (eg. calcium disodium EDTA)
- Stabilizing agent and thickening agent: Stabilizes the food system by thickening the product to the required consistency and gives the food more body (eg. xanthan gum, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium carboxymethylcellulose)
- Colouring agents: Adds appealing appearance and restores colour loss during processing.
Comparison of Alternatives
| Miracle Whip Original Spread | Miracle Whip calorie-Wise Spread | Miracle Whip Fat-Free Spread |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| ||
Both alternative products contain less fat compared to the original product, which could account for the differences in calories per serving size in each product. In addition, fats play a large role in the flavour, texture and colour of the products [8]. Thus, the two alternative products included fat substitutes to compensate for the decrease of fats content in their products. To further reduce the fat content, the fat-free product needed to use less of certain ingredients. For example, soybean oil is listed as a 5th ingredient on the list, while the other two products listed soybean oil as a 2nd ingredient on the list. These other ingredients that were lowered in amount may contribute to the characteristics and preservation of miracle whip. Thus, the additional additives and fat substitutes seen in the fat-free product are to compensate for its lower amounts of fat and certain ingredients.
Labels
All three products meet the labelling regulatory requirements enforced by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA)[9] . A description of the information found on the labels and the regulatory requirements that were met are summarized in the table below.
Table 4: Label description and regulatory requirements
| Miracle Whip Original Spread | Miracle Whip Calorie-Wise Spread | Miracle Whip Fat-Free Spread | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bilingual labelling |
| ||
| Common Name |
| ||
| Net Quantity |
| ||
| Identity of Business |
| ||
| List of ingredients |
| ||
| Nutritional facts |
| ||
| Legibility and location |
| ||
| Irradiated Foods |
| ||
| Sweetners |
| ||
| Allergens |
| ||
| Date Marking/Storage Life/Durable Life |
| ||
| Country of origin |
| ||
| Claims | “No artificial flavours or colours”
The product meets the requirements to claim because the product does not contain any additives that alter the "natural" status of the flavouring and colouring[11]. |
“Lower in calories” and “Less calories”
The product meets the requirements to claim because the product (30 g calories per serving size of 15 ml) contains 25% less calories than miracle whip original (40 g calories per serving size of 15 ml)[12]. “No artificial flavours or colours” The product meets the requirements to claim because the product does not contain any additives that alter the "natural" status of the flavouring and colouring[11]. |
“Fat free”
The product meets the requirements to claim that it is “fat free” because each serving contains less than 0.5 g of fat per serving size[13]. “Less calories” The product meets the requirements to claim because the product (15 g calories per serving size of 15 ml) contains more than 25% less calories than miracle whip original (40 g calories per serving size of 15 ml)[12]. “No artificial flavours” The product meets the requirements to claim because the product does not contain any additives that alter the "natural" status of the flavouring[11]. |
| Kosher Label (not one of the labelling requirements enforced by the CFIA) |
| ||
References
Please use the Wikipedia reference style. Provide a citation for every sentence, statement, thought, or bit of data not your own, giving the author, year, AND page.
Note: Before writing your wiki article on the UBC Wiki, it may be helpful to review the tips in Wikipedia: Writing better articles.[15]
- ↑ Smith, Andrew (2007). The Oxford Companion to American Food and Drink. USA: Oxford University Press. p. 370. ISBN 9780195307962.
- ↑ "Foods Division 7". Justice Laws Website. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Fat Replacers in Food". HealthLinkBC. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Sugar Substitutes". Government of Canada. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "List of Permitted Food Additives". Government of Canada. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Sugar Substitutes". Family Doctor. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Food Additives". Canvas FNH 200 942. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ↑ "Addressing the sugar, salt, and fat issue the science of food way". Nature. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "Food labelling for industry". The Government of Canada. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ "How Long Does Mayonnaise Last?". EatByDate. 2012. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 "Method of production claims on food labels: Nature, natural". Government of Canada. March 8, 2019. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Specific nutrient content claim requirements: Energy and calorie claims". Government of Canada. January 15, 2019. Retrieved July 19, 2020.
- ↑ "Specific nutrient content claim requirements: Fat claims". Government of Canada. January 15, 2019. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 "Kosher 101". MK. Retrieved July 19, 2020.
- ↑ En.wikipedia.org. (2018). Writing better articles. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Writing_better_articles [Accessed 18 Jan. 2018].
| This Food Science resource was created by Course:FNH200. |
