Course:CONS370/Projects/A review and assessment of the forest management and tourism in Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve, Jilin Province, China
| Theme: A review and assessment of the forest management and tourism in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, Jilin Province, China | |
| Country: China | |
| Province/Prefecture: Jilin | |
| City: Yanbian | |
This conservation resource was created by Chenlu Gu, Hanzhi Pu, Jingyu He. It is shared under a CC-BY 4.0. | |
The Changbai Mountain region is one of the birthplaces of Chinese culture, with a long history, rich cultural relics, and profound cultural deposits. The Changbai Mountain forest area is one of the critical forest areas in China and occupies an important strategic position in the ecological construction and forestry industry development in China. In order to prevent the destruction of forest resources, the Chinese government established the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. Within the reserve, the forest management has gradually changed from a government-owned operation to a combination of government and people's cooperative management, with the forest mainly managed by local committees. The establishment of the reserve is of great importance in terms of biodiversity conservation and in conducting scientific research, teaching practice, and tourism. The rich natural resources and the unique natural environment have made Changbai Mountain a nature museum. The tourism industry around the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve is gradually flourishing, with the local government seizing the opportunity to develop tourism resources. However, at the same time, the government should also consider the well-being of the people and take a longer-term view of forest management and tourism development in Changbai Mountain.
Keywords: Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve; forest management; tourism; local communities; Korean Nationality.
Description
Environmental Condition
Geographical condition
Changbai Mountain Biological Reserve is located in the southeastern part of Jilin Province, Northeast China, with an altitude of 720 - 2691 meters. The geographical coordinates are east longitude 127 42'55' to 128 16'48", north longitude 41 41'49' to 42 25′18″. The maximum length of the whole area is 80 km, and the widest area is 42 km, with a total area of 196465 hectares, among which the forest area is 16081 hectares, the grassland is 5683 hectares, the surface of Tianchi is 402 hectares, and the forest coverage rate is 87.9 hectares. It is one of the biggest natural reserves, with the forest ecosystem as the main protection object[1]. .Additionally, the river network in the Changbai Mountain Natural Resources Reserve is densely distributed, mainly based on the Songhua River system[2] .
Climate condition
The Changbai Mountain Natural Reserve belongs to the continental climate zone, with the characteristic of short and cool summer while long and cold winter. The average annual temperature is 3~7℃, and the lowest temperature has been minus 44℃. Moreover, there is a prominent characteristic that the climate in Changbai Mountain changes with the altitude[3].
Natural resources
There are many natural resources in the Changbai Mountain Natural Reserve, including animal resources, plant resources, and tourism resources.
- There are a wide variety of wildlife animals, among which 1578 species belong to 52 orders, 258 families. Besides, there are 58 species of animals under state key protection[4].
- Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve belongs to the Changbai Mountain flora with abundant plant resources, including subtropical, temperate, sub-cold, and polar plants. The vegetation types in this area are mainly composed of Pinus broad-leaved forest, coniferous forest, Yuehua forest, meadow vegetation, and alpine tundra vegetation, and four vegetation distribution zones are formed from bottom to top, which has apparent vertical distribution law[5].
- The Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve is also rich in tourism resources, including magnificent volcanic landscapes, unique snow, and ice scenery, numerous waterfall lakes, and volcanic mineral spring. Etc. In addition, Changbai Mountain Natural Reserve has also developed many facilities to make good use of natural resources to develop tourism[2].
History
Human activities in Changbai Mountain can be traced back to Indigenous society, but the historical establishment of Changbai Mountain began in the Western Han Dynasty[6].
In 1950 - The People's Republic of China set up the Changbai Mountain Forest Police Team in Changbai Mountain.
From 1953 to 1954 - The Ministry of Forestry of China conducted surveys and plans on the forest resources of Changbai Mountain.
In April 1960 - The Changbai Mountain Reserve was formally established. It is one of the earliest and very important nature reserves in China.
In November 1960 - The Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve Administration of Jilin Province was established.
In 1972 - China strengthened the protection and management of the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, giving full play to its important role in maintaining water and soil, conserving water sources, improving the environment, and maintaining the ecological balance.
In January 1980 - The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) officially approved the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve to join the International Biosphere Reserve Network and listed it as one of the world's natural reserves.
In August 1982 - The People's Government of Jilin Province readjusted the scope of the protected area and determined the area of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve to be 190582hm2[7].
In July 1986 - Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve was promoted to a national level of protection.
In November 1988 - The Sixth Standing Committee of the Seventh Session of the People's Congress of Jilin Province passed the "Regulations on the Management of Jilin Changbai Mountain National Nature Reserve," which was the first to realize one region, one law among nature reserves in China.
In August 1992 - Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve was appraised as an A-level nature reserve of international significance by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
In 2003 - Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve was rated as one of the 28 environmental monitoring sites in the world by ten international organizations, including the International Man and Biosphere, Man and Geographic Circle, and Mountain Research Initiation Organization.
In June 2005 - The Changbai Mountain Protection and Development Management Committee was established.
In January 2006 - Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve was included in the first batch of "China National Natural Heritage Preliminary List" by China. It was rated as China's national natural heritage by the Ministry of Construction.
The Korean Nationality
The Korean nationality is one of the ethnic minorities in China. Its population is mainly distributed in Jilin, Heilongjiang and Liaoning provinces which are in the Northeast China. They mainly live in Tumen River, Yalu River, Mudanjiang River, Songhua River, Liaohe River and Hunhe River Basin. Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture, Jilin Province, is the largest Korean nationality inhabited area. According to the census results in 2000, the population of Yanbian is 2.21 million, of which 800000 are Chinese Koreans, accounting for 41.6% of the total Korean nationality population in China[8]. These Chinese Koreans are the cross-border ethnic groups, which gradually came into being by moving into and settling in Northeast China from the adjacent Korean Peninsula. In 1982, the national census found that as early as the late Ming and early Qing Dynasty, some Chinese Korean ancestors had settled in Jilin Province[9]. The Korean nationality has its own language and writing which belongs to Altaic language family. The Chinese Koreans are hardworking and brave, they have actively participated in the anti-imperialist and anti-feudal struggles at all stages under the leadership of the Communist Party of China and made their due contributions to the establishment of new China. At the same time, the Korean nationality has contributed to the development of agriculture in Jilin Province. As a rice production area in Northeast China, the rice fields in Yanbian account for 22.17% of the whole Northeast China. The widespread development of rice fields in the cold northeast indicates that Jilin Province, which has been closed for hundreds of years, has entered a comprehensive development stage[10]. [You need to explain what this last sentence means.]
Tenure arrangements
| Years | Tenure arrangements |
| 1931-1945 | Japanese imperialism monopolizes Tohoku forestry. During these 15 years, the forest area of the Tohoku forest area decreased by 18%[11]. |
| 1945-1949 | After the founding of New China, in the late liberation period, Changbai Mountain forest became national property, and timber was mainly used for military and infrastructure. |
| 1952-1956 | The government allows local aborigines to reserve land near their houses. Other lands are collective forests owned by the government. People own the resources and trees on their own land, but they have no right to decide what trees to plant on the land[6]. |
| 1962 | The People's Committee of Jilin Province approved and forwarded the Forestry Department report and adjusted some divisions of the protected area. |
| 1968 | The Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve Administration was revoked, and the management stations were delegated to Antu, Changbai, and Fusong counties[6]. |
| 1972 | The Jilin Provincial Revolutionary Committee took back the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve Administration Bureau and was directly led by the Jilin Provincial Forestry Bureau. |
| 1978-1991 | The government divides forests into collective forests, state-owned forests, and household plot forests. The national government restricts logging, and the rights of indigenous peoples are restricted. |
| 1991-1998 | The government began to auction the forest land near Changbai Mountain, but the purchaser only has the management right, and the state still owns the ownership of the forest land. |
| 2003 | The government issued a "community-in-household" policy, dividing some collective forests into household plot forests, and the rights and interests of local aboriginals were improved. |
| 2005 | The Jilin Provincial Party Committee has increased the protection of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, accelerated the cultivation of Jilin Province's advantageous tourism industries, unified planning, unified protection, unified development, and unified management of Changbai Mountain, and promoted the development of local forestry and tourism, and also contributed to the economic development of indigenous people. |
Administrative arrangements
Forest Management Institutions
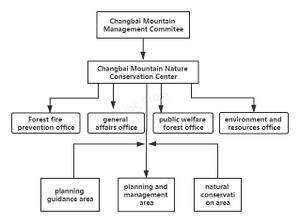
Forest management in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve is usually carried out by forest farms. In 2006, in order to conduct unified management of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, the Chinese government decided to establish Changbai Mountain Management Committee, which is tantamount to the provincial administration and has the full authority to deal with forests relevant issues, such as planning, conservation, exploitation, and management[4]. Usually, conservation work is conducted by Changbai Mountain Nature Conservation Center. Besides, there are four executive departments under the committee, respectively forest fire prevention office, general affairs office, public welfare forest office, and environment and resources office. The concrete functions of Changbai Mountain Management Committee are as followed:
- Comprehensively protecting the natural resources (including land, woodland, grassland, waters, animals, plants, minerals), natural environment, and natural history sites in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve[4].
- Preserving, saving, and proliferating precious and rare biological species, and carrying out scientific research to explore ways of rational utilization of natural resources, further building protected areas into science popularization bases and environmental monitoring bases[4].
- Carrying out propaganda and education, popularize the knowledge of nature protection, organize relevant units inside and outside the region to jointly protect natural resources and natural scenery, and maintain the balance of natural ecology[4].
- In conjunction with the local people's government to organize relevant units within and outside the region to formulate a forest fire prevention convention, jointly do a good job of forest fire prevention[4].
- Carrying out the overall construction plan to carry out the construction, supervise and manage the construction in the management area[4].
Scope of jurisdiction
The total scope of jurisdiction is divided into three parts, respectively planning guidance area, planning and management area, and natural conservation area[4]. The planning guidance area is a coordination area of about 13479 square kilometers (including most of the rives); and the planning management area is a direct management area with 3278 square kilometers (including some parts of the nature reserve and mainly tourism service base, theme function area and other areas under unified management according to planning needs); and the nature reserve is a control area of 1964.65 ㎡[4].
Tourism management Institutions
Changbai Mountain Tourism and Culture Institution
On April 23, 2019, the Party committee of Changbai Mountain Management Committee decided to establish the branch committee of tourism and culture institution of Jilin Province Changbai Mountain nature reserve. Internal departments include Comprehensive Department, Market Management and Comprehensive Law Enforcement Supervision Department, Tourism Publicity and Marketing Department, Cultural Department, Cultural relics Department and Industrial Development Department[2].
The main responsibilities of the Changbai Mountain Tourism and Culture Institution:
- Formulate and organize the implementation of regional tourism, cultural undertakings and industrial development plans, and be responsible for promoting the integrated development of industries.
- Guide and coordinate important tourism and cultural festivals, and promote foreign cooperation between tourism and cultural industries.
- Supervise the tourism and cultural market, promote the construction of the credit system of the tourism and cultural industry, regulate the tourism and cultural market according to law, and supervise the comprehensive law enforcement work of cultural markets in various districts.
- Guide and coordinate the management, protection, rescue, research and publicity of cultural relics, as well as the protection and publicity of intangible cultural heritage.
Undertake the responsibilities of safety production management of the departments, guide and urge enterprises to strengthen safety management, perform the responsibilities of safety production supervision and management in accordance with the provisions of relevant laws and regulations, carry out supervision and law enforcement, and undertake the responsibilities of poverty alleviation[2].
Affected Stakeholders
Indigenous communities
Tourism economy promotes the construction of Korean folk village. With the help of the government, the indigenous people established folk villages to attract tourists to experience Korean culture. The architecture of Changbai Korean Folk Village fully reflects the traditional customs and style of the Korean people, which organically combines the Korean culture, Changbai Mountain Culture and rural environment. In terms of industrial development, Changbai Korean folk village mainly focuses on tourism development, supplemented by ecological agriculture, which greatly enriched the tourism market, promoted the protection of tourism folk customs, and also led to the development of local economy[12]. In 2019, Naitoushan village in Antu County, Jilin Province received 150000 tourists. During the peak period of visiting the memorial hall, it can receive nearly 2000 tourists a day, with an increasing annual per capita income of 5000 yuan[13].
In the context of the vigorous development of tourism, the B & B market has become increasingly hot. Until August 2016, the number of Internet searches for B & B has exceeded that for hotels[14]. Indigenous people seize the business opportunities and set up characteristic B & B in succession. Changbai Mountain B & B culture is a highlight of regional culture, which makes tourists feel the local customs and the warmth of home, and also plays a vital role in the development of tourism. The theme room with Korean characteristics combines the color of Korean nationality. The Chinese Koreans are good at singing and dancing, and their national colors are also very gorgeous, such as red, blue, yellow; there are a bunch of hot peppers hanging in front of the national houses; as a national musical instrument, drum is used in the theme room to give tourists a close experience[12]. Through the characteristic design, the Korean nationality culture and national customs are better publicized, the economic development of the indigenous communities is promoted, and the environmental protection awareness of the public is also aroused.
The beautiful natural scenery of Changbai Mountain attracts tourists from home and abroad, but these people are usually not familiar with the traffic and characteristic areas of Changbai Mountain reserve. The indigenous people of Changbai Mountain begin to become tour guides, they provide tourists with services such as chartering and introducing scenic spots, which can make tourists feel convenient. Tourists pay the corresponding fees to these tour guides, which provide more employment opportunities for the indigenous community. Even the indigenous people with low education background, as long as they are familiar with Changbai Mountain reserve, they can provide help for tourists. The increase of employment rate not only promotes economic development, but also maintains local stability.
Changbai Mountain catering industry also has a good development. The local food in Changbai Mountain area is mainly northeast and Korean. Northeast flavor is mainly stew, salad and pickles, staple food to all kinds of pasta in the majority. Korean flavor is mainly Korean barbecue, dog meat, pickles, soy sauce soup, with rice, millet and grains as the staple food[15]. With the increasingly fierce competition in the catering industry of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, the marketing concepts of indigenous enterprises are constantly updated, from using the existing products to find customers, and gradually developed to market demand-oriented, flexible marketing[15].
Interested Outside Stakeholders
Academy of science
Given that Changbai Mountain is abundant in various resources and has a complex ecosystem, it is a significant area for scientific research. For example, there is one temperate forest ecological function protection and research base located in the northernmost area of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, which focuses on monitoring forest and wildlife resources, active protection, and rescue of rare species of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. Besides, the scientific research base also cooperates with local people to research the cultivation techniques of fungi, fish farming technology, etc[16]. As a result, the Changbai Mountain forest economic processing industry has dramatically developed. To be specific, processing forest resources, such as fungi and Chinese medicinal materials using the developed technology, further promoting the increase of local people’s income.
Tourists
Changbai Mountain has beautiful scenery, such as volcanoes and rivers, attracting many tourists to enjoy the scenery. Besides, Changbai Mountain Area neighbors Korea, which makes it have unique ethnic customs. There are exhibitions and lectures on the natural environment and historical development of Changbai Mountain, further interacting with local people, experiencing local life, etc. Also, Changbai Mountain has been the primary source of ginseng since ancient times, and ginseng collection has become an essential part of Changbai Mountain tourism[2].
Investors
Changbai Mountain has excellent potential for tourism development and has attracted large numbers of tourists since the establishment of the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. There are 13 registered travel agencies in Changbai Mountain Protection and Development Zone, including one international travel agency. Changbai Mountain is famous for its heavenly pools, waterfalls, grand canyons, hot spring groups, alpine gardens, and typical mountain vegetation's vertical distribution[6]. The unique natural environment of Changbai Mountain has attracted many investors, and a large number of hot spring hotels have been opened at the foot of Changbai Mountain[17]. In addition, investors have established ski resorts and fog rafting, and other recreational facilities. According to the different travel resources characteristics, they have opened special lines for scientific research travel in Changbai Mountain, memorable lines for photography tourism, unique lines for winter crossing Changbai Mountain, and special lines for high-end ski tourism to meet the needs of travelers at different levels, forming a complete tour of Changbaishan.
Also, Changbai Mountain is famous for its high-quality ginseng. Ginseng is the main export product of Jilin Province for foreign exchange earning. In the province's agricultural exports, ginseng is second only to corn. Finances at all levels can make a total of more than 100 million yuan in profits and taxes from the acquisition of fresh ginseng, red participation in labor and operation. In the pharmaceutical industry, ginseng products' profit and the tax rate is about 40%, realizing a profit and tax of more than 100 million yuan. Ginseng has also won the favor of investors.[4]
State-owned logging company
Baihe Forestry Bureau and Lushuihe Forestry Bureau are both state-owned forestry enterprises. State-owned enterprises will implement forest management strategies such as tending and logging. The 18 state-owned forestry bureaus and four forestry management bureaus in the Changbai Mountain forest area plan to carry out forest ecological restoration in the Changbai Mountain forest area in three years, plan to implement afforestation renewal of 15,000 mu, develop 7.2 million mu of forest tending, and implemented the second phase of the natural forest protection project to cultivate 2.1 million mu of reserve resources.
Discussion
Tourism
Aim
Due to the relatively late development history, the economy of the surrounding areas of Changbai Mountain is relatively backward, and the tertiary industry is undeveloped. Changbai Mountain has a good natural ecology and landscape scenery like complete forest ecosystem and rich biological diversity, as well as the unique Korean folk customs, which has a great attraction to tourists from South Korea, Japan and Southeast Asia[14].
Assessment
Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve has comprehensive tourism service and reception facilities, which can basically meet the different needs of tourists at home and abroad. The re-establishment of Changbai Mountain tourism management system has also laid a good foundation for the development of tourism. In 2007, Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve received more than 1.2 million tourists, and the total revenue of tourism reached 100 million yuan[18]. The development of tourism in Changbai Mountain reserve is successful. In 1995, when the national tourism administration carried out Chinese landscape tourism, Changbai Mountain was regarded as one of the five meeting points. In 1998, Changbai Mountain was listed as a national tourist attraction. In 2002, Changbai Mountain was rated as one of the top ten famous mountains in China. In 2007, it was rated as a 5A tourist attraction by the National Tourism Administration. In many countries in the world, Changbai Mountain is more famous than Jilin Province[18].
Forest and resource management
Aim
China's State Council proposed in the plan to strengthen the management of critical urban forest areas forest management and protection, to completely stop the primary logging of natural forests in the Changbai Mountain forest area from 2015, and to build a national reserve base of strategic timber resources.
Assessment
The forest management in Changbai Mountain has been very effective. Over the past 68 years, the Changbai Mountain forest project has produced a total of 118 million cubic meters of commercial timber for the country, creating a total forestry industry output value of 100 billion yuan and an industrial output value of 35 billion yuan, making it a substantial commercial timber base for the new Chinese nation. The evaluation report of Jilin Forestry Research Institute and China Forest Ecosystem Positioning Research Network Management Center shows that Changbai Mountain forest area is ranked first in Jilin Province in five leading indicators of water conservation, soil conservation, carbon sequestration and oxygen release, nutrient accumulation by forest trees, and purification of the atmospheric environment. The assessed value of ecological service function is 323.3 billion yuan, accounting for 41.2% of Jilin Province[6].
Investigations show that the herbivorous and omnivorous wild animal populations in the Changbai Mountain Reserve have recovered noticeably, and the natural secondary forests of small plant populations such as Korean pine and Fraxinus mandshurica are gradually expanding. So far, a total of 106 ecological protection projects have been implemented, with an investment of 4 billion yuan[2]. Through these investments, the status of environmental protection has been dramatically improved, and the Changbai Mountain Reserve has also created a comfortable habitat and thriving environment for the Chinese Merganser, a national first-level protected animal. The number of Chinese Mergansers in the Changbai Mountain area is increasing, which indicates that the ecological and environmental protection of Changbai Mountain has achieved initial results.
Conflicts and Critical Issues
Because of strict forest laws conducted in China, forests within Changbai Nature Reserve are well protected from damage like logging. However, conflicts still exist in forest protection and eco-tourism in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve.
- The protection task of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve is under increasing pressure from the growing demand for mountain leisure and entertainment. Considering that the eco-tourism in Changbai Mountain is an essential part of local economics, the Jilin government decided to designate Changbai Mountain more than 1500 m as a tourism industry[19]. Besides, to provide good services to tourists, the local government has invested many resources to build roads and hotels and bring more labor to the protected areas to provide various services. The booming tourism industry in protected areas threatens the pristine natural state of forests in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve and accelerates deforestation outside it[19].
- The conflict between wild plant exploration and conservation is aggravating. Wild plants are crucial environmental protection indicators since many plants can be used for food, fuel, and medicinal purposes. At the same time, human activities are crucial to the economic development of the local people, which makes the wild plants more vulnerable to human activities. The development of tourism in Changbai Mountain makes wild medicinal and edible plants a vital part of attracting tourists. Nevertheless, correspondingly, the conflict between wild plant exploration and conservation is intensifying. Changbai Mountain Area has many medicinal and edible plants, but many of them have become rare and endangered[20].
- Another severe conflict is the forest protection within and outside protected areas. The primary aim of establishing the nature reserve is to protect the forests and other natural resources better. To avoid deforestation in the Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, the forests in the surrounding area have been extensively cut down currently[21]. In addition to logging, forests are fell for farming, and other land uses. As a result, the degradation of pristine forests outside nature reserve is faster than that within nature reserves, which is not beneficial for holistic protection[22].
Assessment
Generally speaking, the significance of indigenous communities is high but the influence is low, while investment companies and governments have both high importance and great influence.
Indigenous communities
The establishment of the nature reserve makes the farmlands destroyed by a large number of animals, and affects the economic income of the indigenous people[23]. Similarly, a large amount of lands were incorporated into the scope of the reserve. The prohibition of collecting forest products is also a main reason for Aboriginal opposition. Farmers said that before the establishment of the reserve, they could collect a lot of pine nuts and mushrooms in the mountains. These forest products can not only enrich their diet diversity, but also bring them extra income. However, it has become illegal now[23]. Although most farmers are reluctant to comply with the restrictive rules, they have to do so. The Indigenous Community also has the function of organization and management. The indigenous committee can introduce and publicize the national policies to the local people, educate the them to abide by the law, legally exercise their rights and fulfill their obligations; pay close attention to the indigenous people's life, maintain the public order of the community, mediate conflicts, and build a communication platform between the indigenous people and the government.
Government
- The central government mainly controls the general development direction and policy of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve, but it does not participate in the daily decisions of protected areas.
- Local government plays an integral part in the management of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. The daily work is usually conducted by Changbai Mountain Management Committee, which has the full authority to deal with forestry issues, such as planning, conservation, exploitation, and management[4]. Generally, the committee uses the laws to ensure the progress and supervision of the conservation work in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. Besides, the local government is also in coordination with indigenous communities, ensuring the rights of indigenous peoples are guaranteed while developing. Additionally, local government also formulates policies to attract investment and protect natural resources.
Investors
- Investors invest in a group business model, and the Changbai Mountain development and Construction Group, established by the provincial government, provides the central financing platform for regional development and construction. The availability of these investment funds can provide a financial guarantee for the construction of tourism infrastructure. By then, major projects such as Changbai Mountain Tourism Airport, East Side Road Railway, and Changbaishan Ring Road will be completed one after another. The infrastructure conditions of Changbai Mountain will be significantly improved, and the reception capacity and service level will be significantly improved.
Recommendations
- Applying landscape approach to combine forest conservation within and outside the nature reserve, further better understanding the interactions between departments and landowners to maximize conservation and development value[24]. To be specific, the implementation of forest ecosystem management can be essential to strengthen forest sustainability beyond community rehabilitation[25]. Besides, the eco-tourism industry in Changbai Mountain Area should pay for the protection of forests within and around community rehabilitation[26].
- Poaching and medicine harvesting are the main threats to ecosystem conservation in the Changbai Mountains. China's forest policy has failed to control human activities such as seed harvesting and forest recreation well enough to exacerbate ecosystem damage still. So there is a need to improve China's forest policy, not only for trees but also for forest ecosystems. Ecologically beneficial conservation effects can be achieved if local people are given economic or political rights to participate in forest ecosystem conservation[27].
- Changbai Mountain is not only located in China, it is a transnational mountain range. Only through China's forest management and conservation is not enough. It is necessary to promote cooperation between China and North Korea, jointly set goals, discuss conservation contents, and carry out comprehensive forest management and protection actions. Other international organizations or non-governmental organizations can also participate in this cooperation project, because it has important reference significance for the study of the relationship between environmental threats and forest restoration. Promoting cross-border cooperation can create opportunities for conservation and management actions, which is conducive to the sustainable development of forests in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve[28].
References
- ↑ Yuan, J., Dai, L., & Wang, Q. (2008). State-led ecotourism development and nature conservation: A case study of the Changbai Mountain Biosphere Reserve, China. Ecology and Society, 13(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-02645-130255
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Wang, Q., Zhang, S., & Tang, B. (2020). Changbai mountain natural resources reserve based on ecological footprint theory ecological structure optimization. E3S Web of Conferences, 167, 6002. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202016706002 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name ":4" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Wu, G., Xiao, H., Zhao, J., Shao, G., & Li, J. (2002). Forest ecosystem services of Changbai Mountain in China. Science in China, 45(1), 21-32. https://doi.org/10.1360/02yc9003
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 Jilin Changbai Mountain Protection Development Management Committee. (n.d.). Overview of Changbai Mountain. Retrieved April 16, 2021, from http://www.changbaishan.gov.cn/gk/
- ↑ Yu, D., & Han, S. (2016). Ecosystem service status and changes of degraded natural reserves – A study from the Changbai Mountain Natural Reserve, China. Ecosystem Services, 20, 56-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2016.06.009
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Historical evolution-Jilin Province Changbai Mountain Protection and Development Zone Management Committee. (2016). Management Committee of Changbai Mountain Conservation and Development Zone, Jilin Province.
- ↑ Han, B. (2016). Deep excavation of forest cultural connotation and development of forest tourism products in Changbai Mountain. Journal of Changchun University, 26(4), 46-50.
- ↑ "The Korean nationality".
- ↑ L. I., Hui (2007). "Study on the population security of Yanbian Korean Nationality of Jilin Province [J]". In Northeast Asia Forum. 2.
- ↑ S. H. U, Zhan (2007). "The Forming and the Contribution of Korean Nationality in China [J]". Journal of the Central University for Nationalities (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition). 3.
- ↑ Yu, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Dai, L. (2019). "Exploring the history of the management theory and technology of broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus Koraiensisieb. etzucc.) forest in Changbai Mountain region, northeast china". Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 30(5): 1426–1434.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Zheng, X., & Li, L. (2014). Study on the role of tourism economy in Jilin Province in promoting Korean folk culture. Technology Information, 36, 236-237. doi:10.16661/j.cnki.1672-3791.2014.36.132
- ↑ "The establishment of Changbai mountain folk village makes the villagers richer".
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Tang, X. D., Xu, C. G., & Xu, D. B. (2017). The feasibility analysis of the development of home stay industry in Changbai Mountain. Modern economic information, (30), 475-477. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-828X.2017.30.389
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Zeng,J. (2013). Analysis of Baishan catering industry. Heilongjiang Science and technology information, 28.
- ↑ Changbai Mountain Academy of Sciences. (n.d.). Changbai Mountain scientific research base. Retrieved April 16, 2021, from http://kxy.changbaishan.gov.cn/
- ↑ Tao, Y. (1987). Preservation of the forest resource of Changbai Mountain in relation to human activities. The temperate forest ecosystem, 21-22.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "General situation of tourism development in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve".
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Zhao, J., Li, Y., Wang, D., & Xu, D. (2011). Tourism-induced deforestation outside Changbai Mountain Biosphere Reserve, northeast China. Annals of Forest Science, 68(5), 935-941.
- ↑ Qu, B., Li, W., Chen, Y., & Liu, J. (2011). Protection versus culture-driven exploitation of wild plant resources: The case on changbai mountain. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology, 18(5), 404-411. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2011.577196
- ↑ Shao, G., & Zhao, G. (1998). Protection versus harvest of old-growth forests on Changbai Mountain (China and North Korea): a remote sensing application. Natural Areas Journal, 358-365.
- ↑ Tang, L., Li, A., & Shao, G. (2011). Landscape-level forest ecosystem conservation on Changbai Mountain, China and North Korea (DPRK). Mountain Research and Development,31(2), 169-175. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-10-00120.1
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Yuan, J., Dai, L., & Wang, Q. (2008). State-led ecotourism development and nature conservation: A case study of the Changbai Mountain Biosphere Reserve, China. Ecology and Society, 13(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-02645-130255
- ↑ Sayer, J. (2009). Reconciling conservation and development: are landscapes the answer?. Biotropica, 41(6), 649-652.
- ↑ Tang, L., Li, A., & Shao, G. (2011). Landscape-level forest ecosystem conservation on Changbai Mountain, China and North Korea (DPRK). Mountain Research and Development,31(2), 169-175. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-10-00120.1
- ↑ Farley, J., & Costanza, R. (2010). Payments for ecosystem services: from local to global. Ecological economics, 69(11), 2060-2068.
- ↑ M. Galvin and T. Haller . editors. 2008. People, Protected Areas and Global Change: Participatory Conservation in Latin America, Africa, Asia and Europe. Perspectives of the Swiss National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) North-South, University of Bern, Vol 3. Bern, Switzerland Geographica Bernensia.
- ↑ Tang, L., Shao, G., Piao, Z., Dai, L., Jenkins, M. A., Wang, S., Wu, G., Wu, J., & Zhao, J. (2010). Forest degradation deepens around and within protected areas in east asia. Biological Conservation, 143(5), 1295-1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2010.01.024