Twenty Week Abortion Ban in the USA
Introduction
Abortion can be defined as "the ending of pregnancy by removing a fetus or embryo before it can survive outside the uterus." Women can have abortions for many reasons, for example, the pregnant woman may feel that she is not ready to have a child, or she could have been impregnated by rape and may not want to become a single mother. One very important reason for a woman to decide to have an abortion is the woman's health and safety. It is possible for a fetus to develop a fatal fetal abnormality that may kill the mother. This is called abortion in self-defence. This reason for abortion is most likely to happen twenty weeks post-fertilization, however, many pro-life activists attempt to create a 20-week abortion ban.[1]
Dilation and Evacuation Abortions
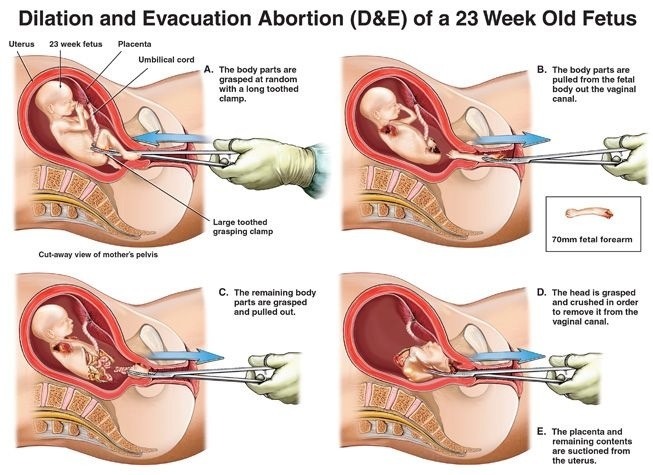
The abortion method illustrated above (a Dilation and Evacuation Abortion) shows one of the types of abortions for fetuses in the second trimester, and may also be referred to as a partial birth. This procedure is recommended for "women diagnosed in the second trimester with a fetus that has severe medical problems or abnormalities"[2]. Most of the women that undergo this surgery do so on a wanted baby, but they are forced to complete the procedure to protect themselves from the fatal fetal abnormality that their fetus has developed that will kill both the fetus and the mother.
Roe v Wade
Roe v. Wade was a court case that changed the USA's federal laws on abortion in 1973. Roe v. Wade was the first to "[recognize] that the constitutional right to privacy extends to a woman’s right to make her own personal medical decisions — including the decision to have an abortion without interference from politicians."[3] From 1973 onwards, abortion was available to women who wanted to terminate the pregnancy for personal reasons, not just for medical reasons.
In some states, medical reasons for an abortion only includes situations where the mother and fetus are in a life-or-death situation. This does not include situations where the fetus is deformed or going to be born with a birth defect that will make the child's life very difficult and/or very short. This means that women whose fetuses develop malformed features that could possibly hinder the child's abilities do not have the option to have an abortion.
20-Week Post-Fertilization Abortion Laws in Different States
Although Roe v Wade made abortion legal on a federal level, some states created very strict laws that limit a woman's ability to receive an abortion, particularly one after 20 weeks. For example, "In 2010, Nebraska passed a law banning abortion care after 20 weeks, under the auspices of concern about fetal pain. Since then, anti-choice advocates have fueled the trend: 14 additional states—Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Kansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Texas, West Virginia, and Wisconsin—have enacted similar bans" [4]. This could be the reason why "the rate of maternal mortality in the U.S. has more than doubled in the past few decades. Whereas 7.2 women died per 100,000 births in 1987, that number swelled to 17.8 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2009 and 2011" [5], and this could largely be due to the pro-life culture that dominates about about fifty percent of the US population.
Nebraska
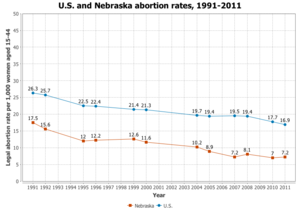
"In 2011, 97% of Nebraska counties had no abortion clinic. 41% of Nebraska women lived in these counties" [6]. Abortion is legal in Nebraska if there is a medical reason behind it, however, Nebraska's legal limit on abortion at a specific gestational age is 20-weeks post-fertilization.
| Code Section | 71-6901, et seq.; 28-325 to 347 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Act, procedure, device, or prescription administered to a woman to produce premature expulsion, removal, or termination of the human life within the womb of the pregnant woman unless the child's viability is threatened by continuation of the pregnancy. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Before viability or if woman is victim of abuse or neglect or if the M.D. has certification in writing that the continued pregnancy is a threat to woman's life, health. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Class III misdemeanor: M.D. who performs abortion in violation of any standards. |
| Consent Requirements | Unemancipated woman under 18 yrs. old or incompetent requires at least 48 hr. written notice to a parent or guardian by delivery or certified mail; court may waive requirements if find woman is mature; parent may authorize abortion in writing. |
| Waiting Period | Voluntary and informed consent of woman 24 hours before abortion, except in emergency (woman must receive state-directed counseling on abortion and other options at least 24 hours prior to the procedure). |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D. |
| Insurance Coverage | Health insurance policies under the ACA may cover abortion only when the woman's life is endangered (optional rider may be purchased for general abortion coverage). |
Alabama
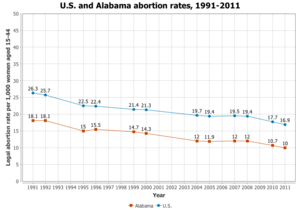
The 20-week abortion law in Alabama has changed since 2010. A second-trimester abortion may not be completed legally for personal reasons in Alabama, an abortion is only permitted if there is a severe medical reason for the abortion. In addition to that, "a woman must receive state-directed counseling that includes information designed to discourage her from having an abortion and then wait 48 hours before the procedure is provided" [7].
| Code Section | Code of Alabama 13A-13-7: Inducing or attempting to induce abortion, miscarriage or premature delivery of woman;
Code of Alabama 26-21-1, et seq.: Parental consent to performing abortion upon a minor; Code of Alabama 26-22-1, et seq.: Abortion of a viable unborn child |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Willfully administers by drug, substance, instrument which induces abortion or miscarriage. Partial Birth Abortion (26-23-1 to 26-23-6): Any physician who performs a partial birth abortion within this state and thereby kills a human fetus shall be guilty of a Class C felony and upon conviction shall be punished as prescribed by law. (except to save life of mother.) |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Necessary purpose to preserve life, health of mother or where fetus is not viable. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Fine of $100 to $1,000 and imprisonment to 12 months; abortion of viable fetus: Class A felony; violation of regulations concerning abortion procedures: Class C felony. |
| Consent Requirements | Written consent of parent or guardian to perform abortion on unemancipated minor or judicial waiver of consent;
New requirements under HB 494:
|
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Abortion of viable fetus must be performed by a physician, in a hospital, with concurrence of 2nd licensed physician as to viability. |
Arizona

In Arizona, there is a limit on abortion after Fetal Viability, except in cases of where the life and health of the mother are in danger. Pregnant women in Arizona considering abortion "must receive state-directed counseling that includes information designed to discourage her from having an abortion and then wait 24 hours before the procedure is provided. Counseling must be provided in person and must take place before the waiting period begins, thereby necessitating two separate trips to the facility" [8].
| Code Section | 13-3603; 36-2152 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | By drug, instrument with intent to procure miscarriage (unless necessary to save mother's life). Partial Birth Abortion: Felony unless to save the life of the mother if no other medical procedure would save the mother's life. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Necessary to preserve life of mother. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Imprisonment 2 to 5 years. |
| Consent Requirements | Written consent of one parent or legal guardian if unmarried or unemancipated patient is under 18, except by court order or medical emergency. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | - |
Arkansas
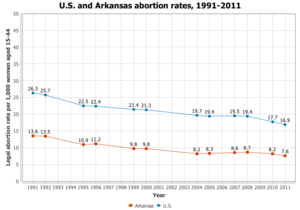
"In 2011, 97% of Arkansas counties had no abortion clinic. 78% of Arkansas women lived in these counties" [9]. Arkansas is another state that does not allow abortions 20 weeks post-fertilization unless it is a safety concern for the mother's life and physical health.
| Code Section | 5-61-101 to 102; 20-9-302; 20-16-601; 20-16-701 to 707; 20-16-801, et seq. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Intentional termination of pregnancy with intent other than to increase probability of live birth or to remove dead or dying fetus, when fetus is viable. Viable fetus defined as one which can live outside the womb; fetus is presumed nonviable prior to end of 25th week of pregnancy. Partial Birth Abortion (§§5-61-201 to 5-61-204): Felony unless to save the woman's life when no other form of abortion would suffice for that purpose. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Abortion of viable fetus permitted when necessary to preserve life of mother, or where pregnancy is result of rape or of incest of minor; written certification by licensed physician required. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Fine to $1,000 and imprisonment 1 to 5 years (Class A misdemeanor). |
| Consent Requirements | Individual seeking abortion must submit to state-directed counseling about the pros and cons of the procedure, and then wait 24 hours before receiving the abortion.
If minor or incompetent, written notice to parent or guardian required at least 48 hours before procedure, except by court order, medical emergency, upon declaration of child abuse, neglect, incest, parents' whereabouts unknown, or parent and minor have not been in contact for at least 1 yr.; informed consent of mother required (§20-16-903) |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Physicians must be licensed to practice medicine in state. |
Georgia
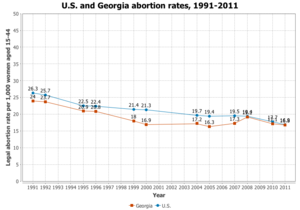
Abortions after the second trimester for personal reasons are illegal in Georgia, however if the mother's life is in danger it is legal if three physicians agree that it is necessary. Georgia has a limit on abortions after fetal viability, however, abortions in the case of medical emergencies are allowed.
| Code Section | 16-12-140 et seq.; 15-11-110 et seq. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | By administering medicine, drugs, or substance or using instrument with intent to procure miscarriage or abortion. Partial Birth Abortion: Unlawful except to save the mother's life when that life is physically endangered and no other medical procedure will suffice to save her life. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | After 1st trimester, must be performed in licensed hospital or health facility; after 2nd trimester, physician and 2 consulting physicians must certify it is necessary to preserve life or health of mother. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Imprisonment 1 to 10 years; partial birth abortion: $5000 and/or imprisonment for up to 5 yrs. |
| Consent Requirements | Except in medical emergency, written, informed consent of parent or guardian of unemancipated minor under the age of 18; parent must have 24-hour notice before scheduled abortion, unless waived or unless minor obtains judicial approval that minor is either mature enough to decide without parents' consent or parents' consent is not in best interests of the minor. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | First trimester: licensed M.D.; second trimester: licensed M.D. and licensed hospital or health facility. |
Idaho
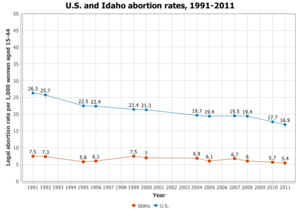
In Idaho, a first and second-trimester abortion is legal for reasons such as rape or incest, however abortion clinics only exist in big cities and not many of them provide second-trimester abortions. If a woman is in need of a second-trimester abortion, she'll have to go to Montana or Oregon [10].
| Code Section | Idaho Code Title 18: Crimes and Punishments, Chapter 6: Abortion and Contraceptives. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | A licensed medical provider who knowingly provides supplies, administers drugs, or uses instrument with intent to produce an abortion other than lawfully has committed a felony. A person without a license has committed this crime for any abortion or attempt. The pregnant woman who knowingly gets or solicits an abortion for herself, other than lawfully provided, also commits a felony. A “partial birth abortion” is also unlawful except when necessary to save the life of the mother when it is physically endangered. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | An abortion is legal in the first and second trimesters if, after a consultation between a licensed medical doctor and woman seeking abortion, the doctor determines that abortion is appropriate considering the various mental, physical, and family factors including circumstances of pregnancy (such as rape or incest). In the third trimester, an abortion is only lawful if necessary to preserve the life of the pregnant woman or the fetus. Additionally, the doctor must consult another physician who agrees it’s necessary. Precautions must be taken to preserve the survival of the fetus, if viable. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | The unlawful abortion provider, medical professional or not, is subject to a fine of up to $5,000 and/or imprisonment for 2 to 5 years. In addition, a health care provider for a first violation can be professionally disciplined with at least a $1,000 civil penalty. A second violation results in his or her license to practice being suspended for six months and a not less than $2,500 civil penalty. Any subsequent violation can result in the revocation of his or her license and a fine of at least $5,000. The woman seeking the abortion can be fined up to $5,000, and incarcerated for 1 to 5 years. |
| Consent Requirements | A woman must give "informed consent" after information about the development of fetus, adoption and other services, risks of the procedure, etc. This consent is also called “biased counseling” by critics. |
| Waiting Period | After receiving the counseling required for informed consent, the woman or teen must wait 24 hours to have the procedures. This puts up a roadblock for women who must travel from rural communities to health facilities that provide abortions. |
| Spousal Notification | The U.S. Supreme Court held that spousal notification laws are unconstitutional in 1992. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | Since 1973, states can’t deny out-of-state residents abortions or other medical care because the Supreme Court found that denial unconstitutional. |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | In the first trimester, the abortion can be performed in a hospital, clinic, or doctor’s office with nearby acute care for complications. In the second trimester, the procedure must be done in a licensed hospital and be in the "best medical interest" of the pregnant woman. A third trimester abortion can only be in a hospital with two doctors concurring on the medical necessity for the woman. |
Indiana
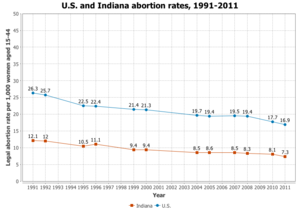
Partial birth abortions are considered an absolute last resort in Indiana. 20-weeks post fertilization abortions are only allowed if the mother is in danger.
| Code Section | 16-34-1-1 et seq. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Any abortion not as provided for in 1st or 2nd trimester. Partial Birth Abortion: A person may not lawfully or knowingly perform a partial birth abortion unless a physician reasonably believes it is necessary to save the life of the mother and that no other medical procedure is sufficient. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | During first trimester with mother's consent based on physician's professional and medical judgement; after first trimester but before viability, permissible with mother's consent and if performed in hospital or surgical center; after viability, procedure necessary to prevent impairment of life, health of mother and performed in hospital with premature birth care unit and with 2nd physician present. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Class C felony; Statute, Class A misdemeanor for not meeting proper consent requirements. |
| Consent Requirements | Written consent of mother, not applicable in emergency; if unemancipated minor under 18 yrs. old, performing abortion not in accordance with written consent of one parent or legal guardian; court can waive parental consent requirement; not applicable in emergency. |
| Waiting Period | After receiving the counseling required for informed consent, the woman or teen must wait 24 hours to have the procedures. This puts up a roadblock for women who must travel from rural communities to health facilities that provide abortions. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | First trimester: professional judgment of attending licensed M.D.; second trimester, before viability: same as first and licensed hospital; after viability: same as second and reasons for procedure regarding mother certified by M.D. to hospital. |
Kansas
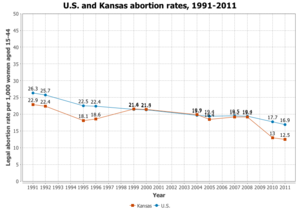
Kansas allows abortions on a non-viable fetus, however past that it is illegal to perform an abortion unless there is a severe medical reason behind it. Kansas states viability starts 22 weeks after the mother's last menstrual period.
| Code Section | Kansas Statutes 65-6701 et seq.: Abortion |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | To perform or induce abortion when fetus is viable, that is, in attending physician's best medical judgment, fetus is capable of sustained survival outside the uterus without extraordinary medical means. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | As long as fetus is not viable (and mother's informed consent obtained); abortion of viable fetus permitted if 2nd M.D. certifies that abortion is necessary to preserve life of mother or fetus has severe, life-threatening deformity or abnormality. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Class A nonperson misdemeanor. |
| Consent Requirements | Informed consent of all women before abortion (not applicable in emergency);
Notice must be given to one of unemancipated minor's parents or guardian (court can waive notice requirement on finding minor sufficiently mature or notice not in minor's best interest) |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D.; 2nd M.D. (not financially associated with 1st M.D.) to certify abortion of viable fetus to preserve life of mother. |
Louisiana

If Roe v Wade were to be overturned, Louisiana would be the first state to ban abortion.
| Code Section | 14:87, et seq. 40:1299.31 to 40.1299.35.18 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Deliberate termination of human pregnancy after fertilization of a female ovum, after viability by any person, even the woman herself, with intent other than to produce live birth, remove ectopic pregnancy, or remove dead fetus. Partial Birth Abortion: Unlawful except when necessary to save life of a woman endangered by physical disorder, physical illness, or physical injury when no other medical procedure would suffice. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | After viability or third trimester, any termination of pregnancy necessary to preserve life, health of mother and/or fetus; Also, 2nd physician must be in attendance for the abortion of a viable fetus. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Crime of abortion: 1-10 yrs., imprisoned at hard labor and $10,000-100,000 fine; Fine of not more than $1000 or imprisonment of up to 2 yrs. for violation (40:1299.31-1299.35.18); A person who kills a viable child during labor shall be sentenced to life imprisonment at hard labor, except when the death of the child results from an express act to save the life of the child or the mother. |
| Consent Requirements | Written informed consent of woman 24 hours prior to abortion; if unemancipated minor, signed consent of parent or guardian or court, except in medical emergency or if judicial consent. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D. must make judgment of advisability or necessity of abortion, shall certify medical reasons for viability abortion. |
Mississippi
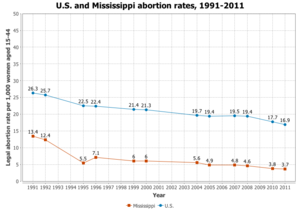
Mississippi has only one abortion clinic in the entire state, and many hospitals deny the employment of physicians who have performed abortions before.
| Code Section | Mississippi Code 97-3-3, 5;
Mississippi Code 41-75-1, et. seq.; Mississippi Code 41-41-31 to 41-41-73 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Willfully or knowingly by means of instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance causing any pregnant woman to abort or miscarry; Partial Birth Abortion: prohibited unless necessary to save mother's life if no other medical procedure would suffice. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Necessary to preserve mother's life; pregnancy result of rape. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Felony: imprisonment 1 to 10 years; if mother dies, murder; if M.D. or nurse convicted, license will be revoked; misdemeanor: $25-200 and imprisonment up to 3 mos. if selling, giving away, possessing or in any manner anything causing unlawful abortion; Partial Birth Abortion: felony, up to $25,000 fine and/or 2 yrs. imprisonment. |
| Consent Requirements | Written informed consent of the mother at least 24 hours before the abortion, except in emergency; unmarried woman under 18 must have written consent of both parents, with exceptions for medical emergency or judicial waiver. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D.; prior advice of two licensed M.D.s required in writing. |
North Dakota

North Dakota is one state on this list whose abortion laws have loosened since 2010. There are now no restrictions before viability in North Dakota.
| Code Section | 14-02.1-01 to 12 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | (1) Non-licensed person performs abortion; (2) if licensed M.D. but doesn't conform to standards for legal abortion; termination of human pregnancy with an intention other than to produce a live birth or to remove a dead embryo or fetus. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | During 1st 12 wks., no restrictions. After viability, necessary to preserve life of mother or continuance would impair her physical or mental health and must be in a hospital. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | M.D.: Class A misdemeanor; anyone not M.D. who performs abortion: Class B felony; if M.D. does not take proper care to preserve life of unborn or born viable fetus: Class C felony; all other violations of N.D. Abortion Control Act: Class A misdemeanor. |
| Consent Requirements | Informed consent of mother as certified by M.D. at least 24 hours before procedure; before viability, if mother is unemancipated minor M.D. must inform both parents or guardian at least 24 hours before minor's consent; or emergency or judicial waiver; after viability, husband's written consent, unless separated, or consent of a parent/guardian if mother is less than 18 years and unmarried, unless procedure is necessary to preserve life, health of mother; court can authorize abortion on minor without parental consent. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D. using medical standards applicable; licensed hospital required after first 12 weeks of pregnancy as well as M.D. must certify facts and have 2 M.D.s concur with his medical judgement for abortion, unless medical emergency. |
Oklahoma
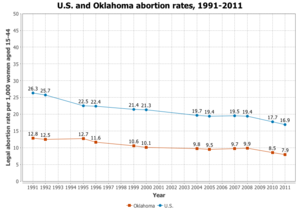
In Oklahoma, "[a] woman must receive state-directed counseling that includes information designed to discourage her from having an abortion and then wait 24 hours before the procedure is provided." [11]
| Code Section | Tit. 63§§1-730 to 741; 21§§713 to 714; 21§861; 21§684. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | (1) Non-licensed person performs abortion; (2) failure to meet standards for legal abortion; (3) taking life of viable fetus unless necessary to preserve life, health of mother or failure to provide medical aid to fetus; purposeful termination of a human pregnancy with intent other than to produce a live birth or remove a dead fetus. Partial Birth Abortion: Physicians shall be fined $10,000 and/or imprisoned for not more than 2 years for performing a partial birth abortion except when necessary to save the mother when her life is endangered by a physical disorder, illness, or injury. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | After viability, necessary to preserve life, health of mother (viability presumed after 24th week). If abortion is self-induced, must be under supervision of M.D.; after viability M.D. required to aid fetus, except in medical emergency. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Person who administers or uses drugs or any other instrument to procure miscarriage unless to save life of mother: 2-5 yrs. imprisonment; if mother is pregnant with unborn quick child and child or mother dies: at least 4 yrs. imprisonment; person not M.D. performing abortion: 1 to 3 years in state penitentiary; anyone aborting viable fetus not to prevent mother's death or health impairment: homicide; willful killing of unborn quick child by injuring mother or any other means (drugs, medicines, instruments): manslaughter. |
| Consent Requirements | Parent of a minor must be notified and give consent. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D.; approved hospital required after first trimester; M.D. must certify necessity of procedure after viability, including factors considered. |
Texas
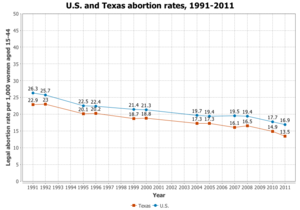
Although Texas is the state where Roe v. Wade took place, it is still a state with very strict abortion laws. Although it is legal to get an abortion in Texas before 20-weeks, it is very difficult to have the procedure done as there are many people against it.
| Code Section | Civ. Stat. §§4512.5, H&S 245.001 et seq. |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | (1) Destroys the vitality or life of child in birth or before (which otherwise would have been born alive); (2) operating a facility without license, failure to meet Board of Health standards, or failure to make reports to Department of Health; (3) act performed after pregnancy with intent to cause termination of pregnancy other than for purpose of birth of live fetus or removal of dead fetus; (4) with public funds except for cases of life endangerment, rape, or incest; (5) after 20 weeks of gestation (or 22 weeks, if calculated from last monthly period), unless necessary to preserve the life of health of the woman. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Abortion during third trimester of viable child permissible only if necessary to prevent death or substantial risk of serious impairment to woman's physical or mental health, or if fetus has severe and irreversible abnormality. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Abortion of viable fetus: imprisonment 5 years to life; operating facility without license: fine $100 to $500 per day, Class C misdemeanor; failure to report as legally required: Class A misdemeanor. |
| Consent Requirements | Parent of a minor must consent and be notified prior to the procedure. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed physician with admitting privileges at a local hospital (within 30 miles); at separately licensed facility (unless necessary to protect life, health of mother). Third trimester: must certify in writing medical indications supporting M.D.'s judgement. Private hospital or facility is not required to make their facilities available for an abortion unless M.D. determines mother's life is immediately endangered. |
West Virginia
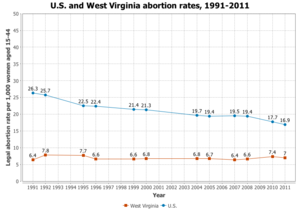
West Virginia has similar abortion laws to many of the states listed above.
| Code Section | West Virginia Code 16-2F-1, et seq.: Parental Notifications of Abortion;
West Virginia Code 33-42-8: Partial-Birth Abortions Prohibited; West Virginia Code 61-2-8: Abortion (held unconstitutional by Doe v. Charleston Area Medical Ctr., Inc. 529 F.2d 638 (4th Circ. 1975)) |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | Administer substance or use means with intent to destroy unborn child or produce abortion; unless in good faith to save woman or child. Partial Birth abortion: any person knowingly performing a partial birth abortion other than to save the life of mother endangered by a physical disorder, illness, or injury is guilty of a felony and shall be fined $10,000 to $50,000 and/or imprisoned not more than two years. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Necessary to save life of mother or fetus. performed by an M.D. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Performing illegal abortion: felony: imprisonment 3 to 10 years; if mother dies: murder; violation of minor notification requirements: misdemeanor, $500-1,000 fine and/or up to 30 days in county jail. |
| Consent Requirements | 24 hours actual notice or 48 hours constructive notice to parent/guardian of minor under 18 who has not graduated from high school, minor can petition court for waiver of notification or it may be waived by another M.D. not associated with attending M.D., unless emergency. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | - |
Wisconsin
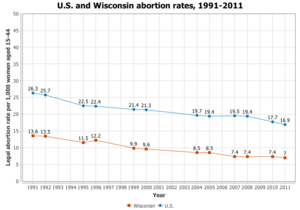
Wisconsin defines legal abortion as an abortion that is necessary to save the life of a mother.
| Code Section | 940.04; 48.375 |
| Statutory Definition of Illegal Abortion | (1) Intentionally destroys life of unborn child; (2) causes death of mother during procedure; (3) mother intentionally destroys unborn child or consents to same; (4) mother intentionally destroys life of unborn quick child or consents to same. |
| Statutory Definition of Legal Abortion | Necessary to save life of mother or advised by two other M.D.s as necessary. |
| Penalty for Unlawful Abortion | Person other than mother performs abortion: imprisonment up to 3 years and/or fine to $5,000; mother dies or intentionally destroys life of unborn quick child: imprisonment to 15 years; mother performs or consents to abortion: imprisonment to 6 months and fine to $200; mother performs or consents to abortion on quick child: imprisonment to 2 years. |
| Consent Requirements | Informed written consent of unemancipated minor as well as informed, written consent of 1 of her parents, or an adult family member, or her guardian, unless the pregnancy is a result of sexual assault, or incest, or a physician believes the minor to be suicidal, or medical emergency, or subject to a judicial waiver. |
| Residency Requirements for Patients | - |
| Physician Licensing Requirements | Licensed M.D., licensed maternity hospital except in medical emergency. |
Feminist Perspectives on 20-Week Bans
Feminism plays a very important role in second-trimester abortions because if a woman does not have access to this kind of abortion, then her freedom is taken away because she does not have the choice to have an abortion. Pro-lifers argue that after viability (often defined as after 20-weeks), an abortion becomes murder based on the assumption that the fetus can feel pain and could survive outside of the womb at this point. Katie Watson calls this the "viability paradox" in her article titled "Abortion Bans Premised in Fetal Pain Capacity." The viability paradox is the idea that "as soon as fetuses can survive outside the womb, the state can force women to keep them inside their wombs."
Abortion and Religion
There are two very different bioethical frameworks when discussing medical decision making; one that is universal to all humans and one that is more relative based on cultural beliefs. In some cultures, a second-trimester abortion is not culturally acceptable and may not be permitted. Religion has a major impact on whether a woman feels comfortable getting an abortion, because if the culture the woman is surrounded by is against abortions, she may feel as though she will be excluded from the community if she gets one. 20-week post-fertilization abortions are particularly touchy topics for pro-life focused religions because by that point the fetus has taken the shape of a baby and that makes pro-life activists feel as though the procedure is more like murder.
Christianity
A 2014 poll noted that 70.6% of Americans identified as Christian [12]; 46.5% identified as Protestant, 20.8% identified as Catholic, 0.5% identified as Orthodox Christian, 1.6% identified as Mormon, 0.8% identified as Jehovah's Witness, and 0.4% identified as other.
The Gospel of Luke 1:44 of the Bible, writes:
“For, lo, as soon as the voice of thy salutation sounded in mine ears, the babe leaped in my womb for joy.”
In Jeremiah 1:5, it says:
“Before I formed you in the womb I knew you, before you were born I set you apart; I appointed you as a prophet to the nations.”
Protestant
A 2013 poll revealed that 75% of white evangelist protestants, 58% of black protestants and 38% of white mainline protestants in the US believed that having an abortion is morally wrong [13].
Many protestants interpreted these excerpts mentioned above to mean that an unborn fetus is, in fact, a baby that has the capability to have feelings and emotions like a human person. Because of that, many protestants are against abortion as they believe that abortion is murder. Due to the large protestant population in the US, this belief is widespread and therefore many women who are in catholic communities may not consider abortion when they have conceived and unwanted fetus.
However, after the verdict was reached on Roe v. Wade, Former Southern Baptist Convention President, W.A. Criswell said "I have always felt that it was only after a child was born and had a life separate from its mother that it became an individual person," and followed with "it has always, therefore, seemed to me that what is best for the mother and for the future should be allowed." Criswell would later reverse himself on this position [14].
Catholic
It is written in the Catechism of the Catholic Church that "[h]uman life must be respected and protected absolutely from the moment of conception." Because of this, many Catholics are against abortion. In addition, Canon 1398 states that "a person who procures a completed abortion incurs a latae sententiniae (automatic) excommunication."[15]
It is written in section 13 of Evangelium Vitae by John Paul II in 1995:
| "In order to facilitate the spread of abortion, enormous sums of money have been invested and continue to be invested in the production of pharmaceutical products which make it possible to kill the fetus in the mother's womb without recourse to medical assistance. On this point, scientific research itself seems to be almost exclusively preoccupied with developing products which are ever more simple and effective in suppressing life and which at the same time are capable of removing abortion from any kind of control or social responsibility.
It is frequently asserted that contraception if made safe and available to all, is the most effective remedy against abortion. The Catholic Church is then accused of actually promoting abortion because she obstinately continues to teach the moral unlawfulness of contraception. When looked at carefully, this objection is clearly unfounded. It may be that many people use contraception with a view to excluding the subsequent temptation of abortion. But the negative values inherent in the "contraceptive mentality"-which is very different from responsible parenthood, lived in respect for the full truth of the conjugal act-are such that they in fact strengthen this temptation when an unwanted life is conceived. Indeed, the pro- abortion culture is especially strong precisely where the Church's teaching on contraception is rejected. Certainly, from the moral point of view contraception and abortion arespecifically different evils: the former contradicts the full truth of the sexual act as the proper expression of conjugal love, while the latter destroys the life of a human being; the former is opposed to the virtue of chastity in marriage, the latter is opposed to the virtue of justice and directly violates the divine commandment "You shall not kill". But despite their differences of nature and moral gravity, contraception and abortion are often closely connected, as fruits of the same tree. It is true that in many cases contraception and even abortion are practised under the pressure of real- life difficulties, which nonetheless can never exonerate from striving to observe God's law fully. Still, in very many other instances such practices are rooted in a hedonistic mentality unwilling to accept responsibility in matters of sexuality, and they imply a self-centered concept of freedom, which regards procreation as an obstacle to personal fulfilment. The life which could result from a sexual encounter thus becomes an enemy to be avoided at all costs, and abortion becomes the only possible decisive response to failed contraception. The close connection which exists, in mentality, between the practice of contraception and that of abortion is becoming increasingly obvious. It is being demonstrated in an alarming way by the development of chemical products, intrauterine devices and vaccines which, distributed with the same ease as contraceptives, really act as abortifacients in the very early stages of the development of the life of the new human being."[16] |
However, surprisingly enough, a 2013 survey in the Washington Post found that 55% of Catholics believe that abortion should be legal in all/most cases.[17]
Judaism
a 2015 poll found that 2% of the US population is Jewish[18]. That is about 5.4 million people.
There is no reference to abortion in the Torah, therefore, there is no religious statement about whether abortion is morally correct or not. Therefore, it is up to the Jewish population in the US. A poll conducted in 2000 found that 90% of Jews were pro-choice.
Illness, Disability, and the 20-Week Ban
Difficulties arise when fetal abnormalities develop in the womb 20-weeks post-fertilization, however, they are not fatal. In many states, abortions past 20-weeks are only permitted if the mother or fetus's life is in danger before birth. This means, that when a fetus develops abnormalities that will either:
- Not harm the mother, but once the fetus is born it will not survive long
- Not harm the mother, but once the fetus is born it will need intense medical care for the rest of its life
Then the pregnant woman will not have abortion as an option. Some women would see abortion as a method of ending the baby's suffering. [19][20][21]
About 6% of abortions are due to discovered birth defects during tests and ultrasounds[22]. When a pregnant mother discovers that the baby she carries has tested positive for an inoperable birth defect, she must take multiple questions into consideration:
- Is the test false?
- If the test is true, will the birth defect kill the baby?
- If the test is true and the birth defect will not kill the baby, what kind of medical attention would the baby need in order to survive the birth defect?
- Is the medical attention that will save the baby too costly for the parents to afford?
- Will the child be able to lead a happy life?
See Also
Abortion Debate
Pro Life vs. Pro Choice
References
- ↑ http://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2015/sep/22/abortion-bill-20-weeks-senate-republicans-democrats
- ↑ http://www.healthlinkbc.ca/healthtopics/content.asp?hwid=tw2462
- ↑ http://www.plannedparenthoodaction.org/issues/abortion/roe-v-wade
- ↑ http://www.prochoiceamerica.org/media/fact-sheets/abortion-bans-at-20-weeks.pdf
- ↑ http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/has-maternal-mortality-really-doubled-in-the-u-s/
- ↑ https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/state-facts-about-abortion-nebraska
- ↑ https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/state-facts-about-abortion-alabama
- ↑ https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/state-facts-about-abortion-arizona
- ↑ https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/state-facts-about-abortion-arkansas
- ↑ http://statelaws.findlaw.com/idaho-law/idaho-abortion-laws.html
- ↑ https://www.guttmacher.org/fact-sheet/state-facts-about-abortion-oklahom
- ↑ http://www.pewforum.org/2015/05/12/americas-changing-religious-landscape/
- ↑ http://www.pewforum.org/2013/08/15/abortion-viewed-in-moral-terms/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christianity_and_abortion#Protestant_denominations
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canon_1398
- ↑ http://w2.vatican.va/content/john-paul-ii/en/encyclicals/documents/hf_jp-ii_enc_25031995_evangelium-vitae.html
- ↑ https://www.washingtonpost.com/page/2010-2019/WashingtonPost/2013/07/25/National-Politics/Polling/question_11462.xml?uuid=XUun2vUZEeKB-o6Ds4ZMNg#
- ↑ http://www.gallup.com/poll/1690/religion.aspx
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9NxBecfNmKs
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T-7jcdyCFKA
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DWbdovcAE3U
- ↑ https://thisisabortion.wordpress.com/birth-defects/