If the sphere with radius in question  is enclosed by the ellipse, and the radius is maximal, then the surface of the ellipse and the sphere just touch in one point.
is enclosed by the ellipse, and the radius is maximal, then the surface of the ellipse and the sphere just touch in one point.
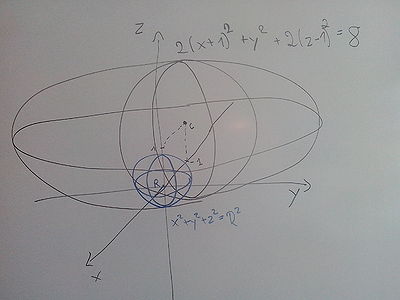
The tangent planes to the surface  and the sphere with radius
and the sphere with radius  are parallel at the points where the surface and the sphere touch.
Hence the normal vectors to the tangent planes are also parallel.
are parallel at the points where the surface and the sphere touch.
Hence the normal vectors to the tangent planes are also parallel.
Regarding the surface equation and the sphere equation as level sets of functions  ,
then the normal vectors to these tangent planes are given by the gradients of the functions
,
then the normal vectors to these tangent planes are given by the gradients of the functions  and
and  .
.
The sphere equation with the origin as center and radius  is
is  . Then
. Then  and
and  . We are looking for
. We are looking for  such that the gradients are parallel,
such that the gradients are parallel,

The second line yields that  or
or  .
.
 leads to
leads to  and using the surface equation we obtain the points
and using the surface equation we obtain the points 
 leads to
leads to  and using the surface equation we obtain the points
and using the surface equation we obtain the points  .
.
These four points are candidates for where the ellipse and the sphere touch. Since we are searching for the radius  such that the sqhere is enclosed in the ellipse, we need the point
such that the sqhere is enclosed in the ellipse, we need the point  with the shortest distance to the origin.
with the shortest distance to the origin.

Since  is the smallest of these numbers, this is the radius
is the smallest of these numbers, this is the radius  of the sqhere.
of the sqhere.



















