Science:Math Exam Resources/Courses/MATH110/April 2011/Question 01 (b)/Solution 1
This statement is false. It reads like the conclusion of Rolle's Theorem; however, Rolle's Theorem has two conditions: that be continuous on a closed interval (in this case the interval ) and differentiable on the same open interval (in this case ). If we drop either of these two conditions, then the conclusion of Rolle's Theorem does not necessarily hold.
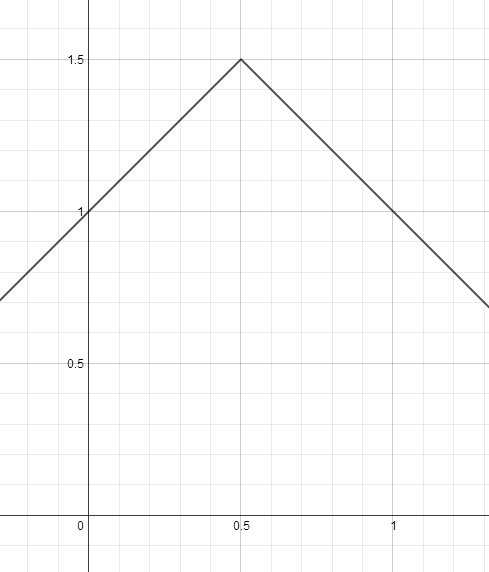
For example, suppose is not differentiable on . Then we can draw the picture:
While this graph satisfies there is no point where the derivative is zero, because the derivative is either 1, -1, or undefined.
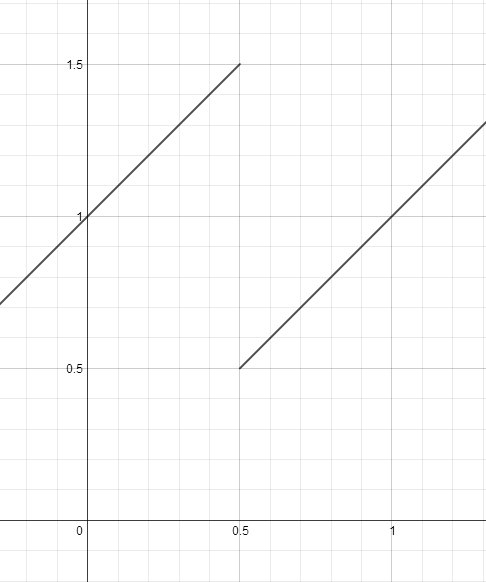
Suppose is not continuous on . Then you can draw a picture like this:
Where clearly the derivative is never zero, even though .
Either example (or a similar example) would suffice to prove the statement false.

![{\displaystyle [0,1]}](https://wiki.ubc.ca/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/738f7d23bb2d9642bab520020873cccbef49768d)