Course:PostgradFamilyPractice/ExamPrep/99 Priority Topics/Red Eye
Red Eye - Key Features
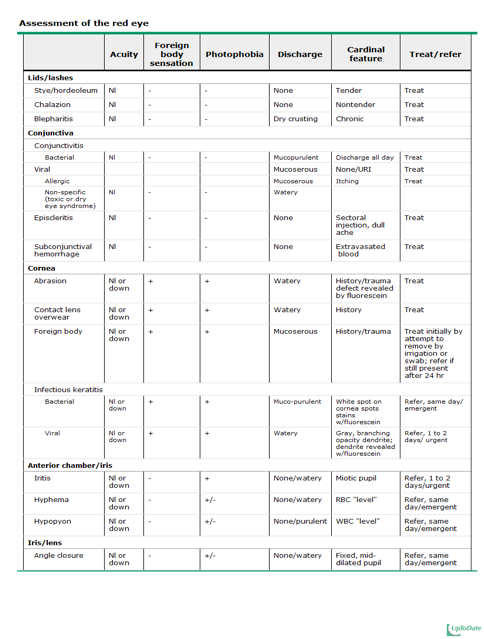
The common culprits: Assessment of red eye courtesy of Uptodate
1. In addressing eye complaints, always assess visual acuity using history, physical examination, or the Snellen chart, as appropriate.
History (general eye questions):
- - Monocular vs binocular
- - Transient (amaurosis fugax) vs acute vs gradual
- - Painless vs painful
- - Foreign body sensation – suggests active corneal process, objective FB sensation when patient resistant to opening eye; “scratchy” or “gritty” more suggestive of conjunctivitis. No FB sensation with iritis/glaucoma.
- - Photophobia – corneal process or iritis
- - Trauma
- - Contact lens wearer – increases suspicion of keratitis
- - Associated symptoms – eg. URTI with viral conjunctivitis.
Physical Exam
- - General observation: ? opening eyes, in pain/distress, dark glasses, tearing/discharge.
- - Visual acuity: always check best corrected visual acuity, use pinhole occlude to help improve vision if refractive error present. Acuity testing: Snellen chart at 20 feet. Near: Rosembaum/pocket vision at 14 inches. Gross testing: reading vision vs form perception vs light perception only.
- - Penlight exam
- o lid, palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea (foreign body, corneal opacity)
- o pattern of redness (affecting both p/b conjunctiva suggests conjunctivitis, vs ciliary flush around limbus suggests iritis, infectious keratitis, acute angle closure glaucoma), hemorrhagic pattern suggests subconjunctival hemorrhage.
- o Fluorescein dye with cobalt blue light - ? corneal process
- o Hypopyon (white cells in anterior chamber) and hyphema
2. In a patient with a red eye, distinguish between serious causes (e.g., keratitis, glaucoma, perforation, temporal arteritis) and non-serious causes (i.e., do not assume all red eyes are caused by conjunctivitis)
a) Take an appropriate history (e.g., photophobia, changes in vision, history of trauma)
See above.
b) Do a focused physical examination (e.g., pupil size, and visual acuity, slit lamp, fluorescein).
Pain
- - While blinking (corneal abrasions / foreign bodies / keratitis)
- - With eye movement (optic neuritis)
- - With headache / nausea (acute angle-closure glaucoma)
- - With brow or temporal pain (temporal arteritis)
- - Photophobia (inflammation of iris & middle layer of eye, corneal irritation)
- - “gritty sensation” (conjunctivitis, corneal abrasion)
- - History of trauma (corneal abrasion)
Change in vision
- - normal vision reassuring (lid disorder, conjunctival process, corneal abrasion, foreign body)
- - red eye with decreased vision – infectious keratitis, iritis, acute angle glaucoma
- - NB the causes of vision loss that are not common “red eye” culprits: retinal vascular occlusion, papilloedema, retinal detachment, cortical blindness etc.
Photophobia
- - corneal process, iritis
Keratitis – inflammation of cornea (photophobia, FB sensation)
- - UV keratitis: eg welding or sunlamp, appears 6-10 hrs after exposure, bilateral redness, photophobia, tearing. Fluorescein staining shows superficial punctuate keratitis.
- - Viral keratitis – often herpes, can be other (eg adenovirus) – FB sensation, photophobia, watery discharge. Herpes simplex: eyelid edema, can have decreased vision. Gray, branching opacity with dentrite seen with fluorescein.
- - Bacterial keratitis – FB sensation, difficulty opening eye, photophobia, mucopurulent discharge, white spot on cornea that stains with flurescein. High risk with contact wearing.
Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
- - Abrupt onset of severe pain, may be frontal or supraorbital headache, redness with ciliary flush, photophobia, decreased/blurred vision, nausea/vomiting, fixed midposition pupil, hazy (cloudy) cornea, elevated IOP (normal 10-20 mmHg, disease 60-80mmHg) NO FB sensation!
Perforation
- - History! Mechanism of injury (projectile, laceration of eyelid or periorbital area, corneal abrasions occurring when hammering metal on metal, etc). Eye pain, acuity may be affected.
- - If you suspect, don’t press on globe! And never measure IOP!
- - Slit lamp exam with fluorescein to check for abrasion, laceration, FB, hyphema, iritis, lens dislocation.
- - Signs: flat anterior chamber, pupil asymmetry or irregularity, extrusion of humor etc.
Temporal arteritis
- - Head ache, jaw claudication, myalgia, fever, anorexia, temporal artery tenderness, TIA/stroke, rapid/profound visual loss (unilaterally initially), afferent papillary defect.
c) Do appropriate investigations (e.g., erythrocyte sedimentation rate measurement, tonometry).
- Bacterial keratitis or conjunctivitis – swab discharge for C&S
- Acute angle closure glaucoma – tonometry (dx 60-80 mmHg)
- Perforation – slit lamp with fluorescein, palpation around orbital rim, check extra ocular movements (NB blowout fractures with trauma).
- Temporal arteritis – ESR or CRP, start prednisone and refer for biopsy of temporal artery if highly suspicious
d) Refer the patient appropriately (if unsure of the diagnosis or if further work-up is needed).
REFER:
- - Acute angle closure glaucoma – emergent – begin treatment to lower IOP – by reducing acqueous humor (topical BB, alpha-adrenergic agonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors), facilitating outflow of aqueous humor (parasympathomimetic miotic agents), reducint volume of vitreous humor (IV mannitol)
- - Perforation – emergent (normal acuity and ocular anatomy can f/u as outpatient within 48 hrs)
- - Hyphema and hypopyon emergently
- - Iritis – urgent
- - Infectious keratitis (bacterial emergent, viral is urgent)
- - Temporal arteritis
PRIMARY CARE:
- - Stye (hordeoleum), chalazion, blepharitis, subconjunctival hemorrhage
- - Conjunctivitis (bacterial, viral, allergic)
- - Dry eye syndrome
- - Episcleritis
- - Corneal abrasion, corneal FB, contact lens overwear – Refer if not better within 24-48 hrs.
3. In patients presenting with an ocular foreign body sensation, correctly diagnose an intraocular foreign body by clarifying the mechanism of injury (e.g., high speed, metal on metal, no glasses) and investigating (e.g., with computed tomography, X-ray examination) when necessary.
- Conjunctival abrasions/lacerations – c/o scratchy FB sensation, mild pain, tearing, and rarely photophobia. Vision preserved unless full-thickness conjunctival laceration. Inspect for and remove foreign particles.
- Corneal abrasions/lacerations – c/o FB sensation, photophobia, tearing. Mechanism of injury important. Exam reveals conjunctival injection, tearing, lid swelling. Relief of pain with topical anesthesia diagnostic of corneal abrasion. Photophobia may be present. Slit lamp exam with fluorescein. If suspicious of penetrating injury, CT of orbit to assess changes in globe anatomy or contour of FB within globe. Consult optho.
- Consider procedural sedation to examine children properly.
4. In patients presenting with an ocular foreign body sensation, evert the eyelids to rule out the presence of a conjunctival foreign body.
- Have patient look down, use q-tip to help evert upper lid. Inspect tarsal conjunctiva. Remove FB with moist cotton bud. May need penlight or magnification. Have patient look up and eyelid with return to normal position.
5. In neonates with conjunctivitis (not just blocked lacrimal glands or ‘‘gunky’’ eyes), look for a systemic cause and treat it appropriately (i.e., with antibiotics).
- Ophthalmia neonatorum = conjunctivitis in neonates up to 30 days old
- 5 main categories: chemical, gonococcal, chlamydial, other bacterial (nongonococcal/nonchlamydial), and viral
- - Chemical: watchful waiting as resolves within 48 hrs
- - Gonococcal: can cause blindness! Prophylaxis with erythromycin ointment at birth. Presents 2-7 days of life. Intense bilateral bulbar conjunctival erythema, chemosis, & copious purulent discharge. Gram stain of discharge: gram negative diplococcic. All infants require admission and evaluation for disseminated disease (i.e., blood, urine, CSF). Tx: single dose of Ceftriaxone 50 mg/kg IV (if no hyperbilirubinemia); Cefotaxime 50 mg/kg IV q8h
- - Chlamydial: Presents 5-14 days of age. Unilateral or bilateral purulent d/c with intense erythema of palpebral conjunctiva. Associated with chlamydial pneumonia. Tx: Systemic erythromycin Base or Ethylsuccinate x 14 days.
- - Other bacterial: Presents within 2 wks of birth; much less common. Hyperemia, purulent discharge, and edema. Usual bugs: S. aueus, nontypeable H. influenza, and S. pneumonia. Tx with topical bacitracin, polymyxin, or neomycin
- - Viral: Herpes simplex types I and II. Presents 6-14 days of life. Bilateral lid edema & conjunctival erythema. Suspicious if associated with mucocutaneous lesions & maternal hx of herpes. Fluorescein exam shows keratitis or corneal dendrites. Requires hospital admission, full sepsis work-up (esp CSF analysis). Tx: Acyclovir 20 mg/kg IV q8h x 14-21 days & topical antivirals (trifluridine 1%, iododeoxyuridine 0.1%, vidarabine 3%)
6. In patients with conjunctivitis, distinguish by history and physical examination between allergic and infectious causes (viral or bacterial)
Allergic conjunctivitis:
- - Symptoms: watery discharge, redness, and itching. Signs: erythematous swollen eyelids, injected & edematous conjunctiva with papillae on inferior conjunctival fornix
Infectious conjunctivitis:
- - Bacterial:
- - Symptoms: painless, unilateral, or bilateral mucopurulent discharge causing eyelids to “stick” on awakening; injected conjunctiva; clear cornea. Signs: chemosis (edema of conjunctiva). NB: preauricular lymph nodes absent, except for gonococcal infections.
- - Viral:
- - Etiology: adenovirus (most common); measles, influenza, mumps; herpes simples / herpes zoster. Symptoms: usually preceded by upper respiratory tract infections, “red eye”, mild to moderate watery discharge; painless; initially unilateral then bilateral. Signs: unilateral or bilateral conjunctival injection, occasional chemosis, and small subconjunctival hemorrhages, and preauricular LA. On slit lamp, follicles on inferior palpebral conjunctiva.
7. In patients who have bacterial conjunctivitis and use contact lenses, provide treatment with antibiotics that cover for Pseudomonas
- Soft contact lenses prone Pseudomonas infection
- Tx: Fluoroquinolone (Ciloxan, Ocuflox) or AMG (Tobrex).
8. Use steroid treatment only when indicated (e.g., to treat iritis; avoid with keratitis and conjunctivitis).
- Do not use ocular steroids in conjunctivitis due to occult herpetic infection. Should only use on ophthalmologist recommendation
- Treatment of iritis includes blocking pupillary sphincter & ciliary body with long-acting cycloplegic agents (homatropine or tropicamide). Ophthalmologic referral needed in 24-48 hrs! Can add prednisone to reduce inflammation.
9. In patients with iritis, consider and look for underlying systemic causes (e.g., Crohn’s disease, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis).
- Iritis = anterior uveitis.
- Uveitis may be divided into four major subsets based upon the etiology of inflammation:
- i. Infections: bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic (lyme disease, syphilis, TB, EBV, CMV, HSV, HIV, candida etc)
- ii. Systemic immune-mediated disease: Ankylosing spondylitis, Behcets, Crohn’s, UC, vasculitis, MS, reactive arthritis etc.
- iii. Syndromes confined primarily to the eye: eg trauma
- iv. Masquerade syndromes: ischemia, leukemia, giant retinal tear, retinoblastoma.
- Symptoms: unilateral pain, maybe bilateral with systemic disease; red eye (conjunctival); photophobia; and decreased vision. No discharge.
- Signs: perilimbal flush (injection greatest around limbus) or diffuse conjunctival injection, no discharge, miotic pupil poorly reactive
- Systemic symptoms can include: arthritis, urethritis, and recurrent GI symptoms. Look for past medical history of exposure to TB, history of genital herpes, history of previous symptoms. Also ask about recent trauma or exposure to welding without goggles.