Course:PHYS341/2022/Project10
Saxoflute
This wiki page will describe the combined instrument of Saxophone and a Flute.
Introduction
Both a saxophone and a flute are part of the woodwind family instruments. However, there are many differences in terms of the presence of reed, the structure of the tube with standing waves, and the characteristics of the sound they produce. Although they have various different features, when a saxophone neck and mouthpiece are combined with a flute body joint, they create a blend of sound which will be further explored below. The concept of a "frankeninstrument" of merging two instruments that sound completely different and are made out of different materials is intriguing and will be further explored throughout this page.
History of Saxophone & Flute

Saxophone was invented in 1846 by a Belgian musician Adolphe Sax. It is a hybrid of brass material and woodwind structures with a single reed mouthpiece. The modern version of the saxophone was manufactured during the 1930s to 1940s with the right-side bell keys being introduced on baritones then on altos and tenors soon after. The modification in tones and mechanical excellence was developed around 1954 to 1974. Saxophones were first used for dance orchestras then eventually used in jazz performances and many more occasions.

Before the invention of Flutes, in the Palaeolithic era of Europe, they were first made out of animal bones and were more alike to recorders as they were vertically held. The more modern version of the flute that was in transverse form was invented in the 16th century during the Renaissance period which started being used in modern orchestras. The name for the instrument was introduced in the middle of the 18th century as flûte traversière in French.

Description of the two original instruments: Saxophone & Flute
A saxophone is divided into 3 main parts: mouthpiece, neck, and body. The mouthpiece has a single-reed that is adjusted by the ligament. It has a (nearly) closed-open conical tube which increases thickness along the tube with displacement not quite sinusoidal that can play up to two octaves and a fifth above ranging from B♭3 to F6.
A flute is also divided into three parts: head joint, body, and B foot joint. The head joint contains a lip plate with an embouchure hole where the player blow in to create sound. It has an open-open cylindrical tube with maximum displacement on each open ends and minimum displacement in the middle that can play up to three octaves ranging from C4 to C7.
How is sound created in the two original instruments
Saxophone
When a reed is blown, the player creates a higher pressure near the mouth leading to the variation of pressure in the tube that the reed reacts to by oscillating up and down. The increase in pressure of the mouthpiece will cause a downward net force on the reed, so the reed will open and more force will get into the reed from the air in the mouth, and vice versa.
Flute
The sound is produced by the continuous air jet that the player produce with their lips as they aim for the far edge on the embouchure hole. The standing wave inside the flute has air oscillating back and forth. During one half of the oscillation when the air is moving out of the opening hole, it will exert force on the airjet that is aiming at the edge will deflect the object upwards leading the air to move out of the instrument. During the other half of the oscillation when air is moving away from the opening hole, it will exert force on the airjet that will deflect the object downward leading the air to get into the instrument. Just like in the reed, the oscillation inside the tube will be reinforced by the airjet.
The Physics behind a Saxoflute
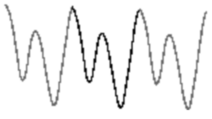
In a saxophone, as it has a close end near the mouthpiece, the air is stationary, which means the compression pulse can only move back along the pipe and the pressure wave will be reflected with no phase change. The sound wave should look like this:
In a flute, as it has an open end near the embouchure hole, the air can move freely, which means the sound pressure is near zero and the pressure wave will be reflected with some phase change. The sound wave should look like this:

Saxoflute
In a Saxoflute, as it has a closed end near the mouthpiece with a cylindrical tube end, the air will be stationary throughout the pipe with a frequency lower than the flute but higher than the saxophone. The predicted sound wave should look like this similar to a clarinet:

The sound frequency of a saxophone shown in a spectrum graph displays a wide range of frequency that goes up to 10000 Hz. Whereas, for a flute, the range of frequency is less as it only goes up to 6000 Hz. Additionally, it is shown that the saxophone has a louder volume with the relatively high decibels in the spectrum graph compared to the flute.
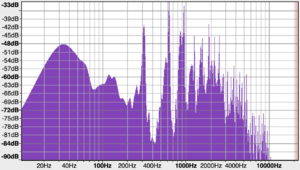
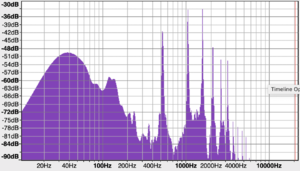
In a spectrum graph of a saxoflute, the frequency range is around 7000 Hz which is between the frequency range of a saxophone and a flute. The sound frequency at 500 Hz has the loudest volume which shows that the sound for a saxoflute is focused towards 500 Hz. This implies that the pitch, volume, and timbre will most likely be between the range of a flute and a saxophone.
Demo Video
This is the link to a demonstration of a Saxoflute being played by Cody Dear.
https://www.instagram.com/p/CbBUjT4gS6u/
References
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Music/flute.html#:~:text=The%20flute%20is%20made%20in,in%20a%20tube%20to%20vibrate.https://www.yamaha.com/en/musical_instrument_guide/saxophone/mechanism/#:~:text=The%20saxophone%20consists%20of%20four,there%20are%2025%20tone%20holes.
https://www.wwbw.com/the-music-room/history-of-the-saxophone
https://www.yamaha.com/en/musical_instrument_guide/flute/structure/