Course:ECON371/UBCO2010WT1/GROUP4/Article 7: Quebec’s Vehicle Emission Law Is Disputed
Summary
Link to the article:
Quebec’s Vehicle Emission Law Is Disputed
The article was about the Quebec's Vehicle Emission was being blasted. The rule imposed increasingly stringent limits on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from cars and light trucks made between 2010 and 2016 that are sold in the province. Under the regulation, a penalty payment of up to $5,000 will be added to the price of any new vehicles that exceeded the maximum emission standard.
The idea of that emission law was actually come from United States. Quebec was the first province in Canada to adopt California’s strict auto emissions standards. The policy maker believed that the emission from vehicles would be cut by about 35 percent in the next six years (2010-2016); the amount of carbon dioxide that the passenger vehicles produce would decrease from 187 grams per kilometer to 127 grams per kilometer by 2016.
There were a lot of people supported the policy and believed that would be one of the best solutions to solved the vehicles emission problems. However,some of the government members said that the policy would deeply affect the vehicles market in Quebec. They believed that many customers will purchase their cars in other provinces since the law merely applied in Quebec. The policy has underestimated the customer revolt.
Nevertheless, there has been no obvious signs of customers revolt after the ruled changed.
Analysis
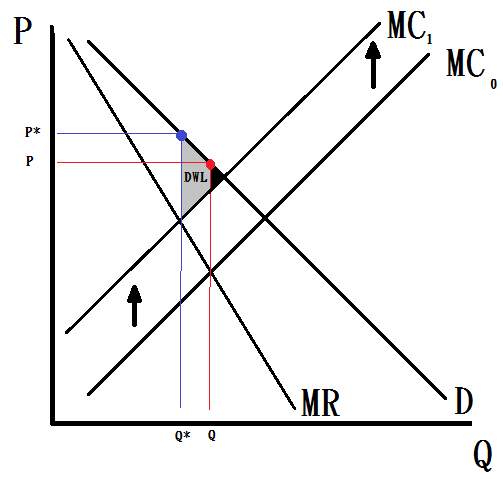
The vehicle emission law has increased the price, as a result, the Marginal Cost Curve will shift up (MC0 to MC1).
(P.S: The price effect to the demand is still elastic since customer can purchase vehicle in other province in Canada.)
After the the Marginal Cost Curve shift up, the price of the vehicle in Quebec will increase and the quantity demand of vehicle will decrease as well.
According to the economic theory, the black triangle is the dead weight lost before the rule changed. After the emission law applied, the dead weight lost increased (the black triangle + the grey area)
In Summary, the vehicle emission law might be effective in terms of the environment. However, the society will suffer a dead weight lost because of the price changed.
Conclusion
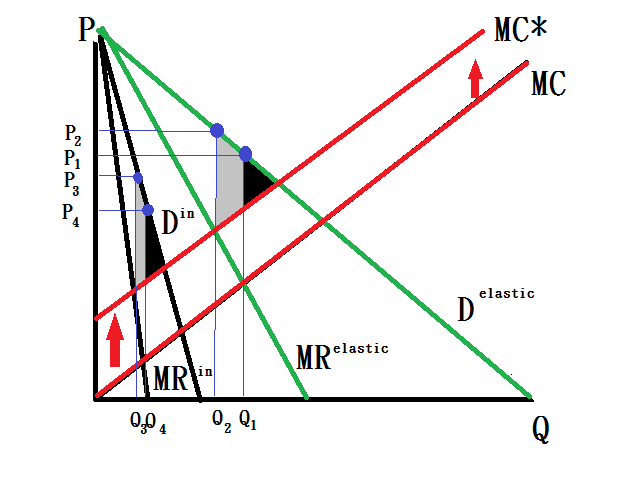
In terms of economics, the Quebec vehicle emission law is a failure since it will increase the dead weight lost in the Quebec's vehicle market. One of the most failures is the government merely applied the law in Quebec. The Canadian government should apply the law in whole Canada, then the consumers cannot escape the price induction unless they purchase the vehicle in other counties. Even the consumers can purchase the vehicle in other countries, they will spend more opportunity cost (such as travel cost). As a result, the price effect on the demand will be more inelastic and the dead weight lost would be smaller.
According to the graph, we can clearly see that an inelastic demand curve will have a smaller induction of dead weight lost.
Prof's Comment
Nice graphs. However, you missed the fact that there is an externality. As such, there is a deadweight loss without the policy, and by shifting the MC curve up, the total DWL is probably reduced.