India's Dowry System
What is a Dowry?
In India, the marital custom of dowry is widely practiced. A dowry is a transfer of wealth from the bride’s family to the groom’s family. Dowries include money, property, jewelry, vehicles, furniture, appliances, clothing, and any sort of gift that can be given or requested.[1]
History of the Dowry Practice
Dowries have been given for centuries now. It is practiced among many cultures through out South Asia.[2] It is mainly practiced among Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs, and Jains. It started off as parents giving their daughters gifts for their comfort. As it is written in the Code of Manu, dowry was a prestigious form practiced by upper castes.[3] In ancient times, kings sent their daughters with dowries to ensure they lived comfortably. When the British ruled India, they prohibited women from owning any property or wealth, thus their entire dowry became their husbands and/or their in-laws. [4]
Why People Practice
Tradition
It is a traditional practice that has been passed down for many centuries. Over time the significance and reason for practicing has changed.
Religious Factors
The significance of dowry is present in many of the religions found in India.
Hinduism
In Hinduism during the wedding, the father does a Kanyadan which is the giving away of the daughter. Kanya means girl and dan means to give, so the meaning of kanyadan is daughter gift, therefore a dowry is a gift for the groom because he is taking the responsibility of their daughter, thus providing him with resources. [1]
Sikhism
In Sikhism, the dowry is called a Dehaj. [5] It started off as being a spiritual dowry; it meant a woman should carry the name of the Lord with her when she starts her new life. However, with social influences and with the influence of greed, the significance of dowry changed.
"O my father! Give me the Lord's Naam (Gur-Giaan, Aatam-Giaan, Shabad-Giaan ...) as my wedding gift / dowry. ||4|| (sggs 78)." [5]
Islam
In Islam, a type of dowry called a Mahr [6] is given from the groom to the bride. The Mahr is paid by the husband to honor his wife and is now taking on her responsibility.
"And give the women their dowries with a good heart..." [Noble Quran 4:4] [7]
Overtime the concept of Mahr changed and became Jahaz. Jahaz is not part of Islam but it is becoming more common among Muslims, especially those living in India. Jahaz is the giving of dowry from the bride to the husband. The change of Mahr to Jahaz can be due to various social factors. [7]
Socioeconomic Factors
In many occasions, parents give dowries for their daughter’s financial security. Although a bride’s family is giving a dowry with good intentions the groom and his family may take advantage of it. There is an expectation of a dowry. A marriage is arranged more on the interests of the parents than the couple. Parents generally try to wed their daughters in higher status families. Women do not receive high levels of education so to better their lives, parents look for a wealthy family and an educated son in law who has a stable job. A dowry increases with the level of education, a job title and any future prospects for the groom. [8] [9]
Why is the Practice of Dowry an Issue?
Patriarchy
The tradition of the dowry system was something that was given out of joy and for the betterment of a female’s life. However through out centuries it became a method of taking advantage of women.
The definition of patriarchy is when in a society or government, men hold the power that women are excluded from. Patriarchy can be seen in the dowry system, because even though the dowry is from and for the bride, the bride is excluded and the men get the power. Women in India have been conditioned to believe that there is no such choice as a divorce; their sole responsibility is to make the marriage work. That is why many comply with demands of increases dowries and why many withstand abuse. [10]
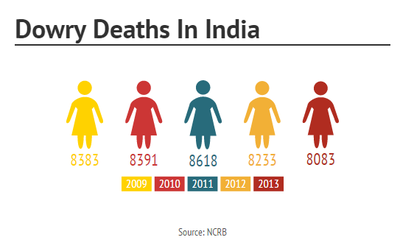
Domestic Violence, Dowry Deaths, and Bride Burning
Due to dowries, many women suffer from domestic violence [11]. Women are murdered or compelled to commit suicide by endless torture by their husbands and in laws in order to extort remaining or increased dowry. Many times families are unable to provide the dowry that is requested by the groom's family. The husband and the in laws behave very cruelly with the bride. The bride may become depressed and in order to free herself, she eventually commits suicide. The methods of suicide are self-immolation, hanging, or poison. If they do not receive the dowry and the bride fights back, she is then murdered. Bride Burning is one of the most common methods used to murder brides. Bride burning is when the husband and/or the in-laws burn the bride and make it look like an accident or a suicide. In other cases, a bride is hung or poisoned and made to look like a suicide.
Other Conflicts or Crimes
Females do not only face issues of dowry during marriage, instead females and their families deal with dowry issues before they are even born.
Sex Selective Abortions
In order to avoid future dowries, parents undergo sex selective abortions and abort any female fetuses.
Female Infanticide
Infant females have been murdered for centuries for several reasons. One main reason is to avoid future dowries.
Education
Many females are deprived of education. However a very common reason for not educating females is dowry. Parents believe instead of spending that money on a education, they can later find their daughter a higher status and educated husband.[10]
Studies reveal that when a women is educated, a higher dowry is paid in order to attract an higher educated male. Many times the groom's family may feel like that the bride will not know or help in house work if she has a career, therefore they need more resources to take care of the household. This could be the reason many families do not educate their daughter, instead they save that money for dowries. [10]
Laws against Dowries
The Indian Penal Code-498A
The IPC-498a is a criminal law that was passed by the Indian Parliament in 1983 [12]. The law states that treating a woman cruelly in order to extort dowry will be punished with imprisonment for a term of three or more years and a fine.
Dowry Prohibition Act of 1961[13]
The 1961 Act prohibited the practice of dowry in many states. Any one who practices the giving or receiving of dowry is punishable. The punishment includes imprisonment not less than five years and a fine that should not be less than fifteen thousand rupees or should equal to the amount of the dowry, depending on which one is more.
The Protection Of Women From Domestic Violence Act, 2005
The Protection Of Women Domestic Violence Act [14] was passed in 2005 to protect women from domestic violence. This law helps in the cases of dowries because many times the reason for domestic violence is an unpaid dowry. This act is a civil law, which means that it is not set to criminalize or penalize individuals, however it is set to protect women from domestic abuse caused by their husbands and/or in-laws.
Foundations against the Dowry System
International Society Against Dowry and Bride Burning[15]
Founded by Mr. Himendra Thakur in 1993, the main goals are to provide awareness and education, to provide support (medical, emotional, financial) to victims and help to avoid paying dowry. They have a six-point program to eradicate dowry and dowry deaths. They attempt to provide opportunities for victims, such as creating a job centre in order to find jobs and become independent.
Other Anti Dowry Foundations and Groups
Many of these foundations and groups work locally to create awareness and change people's negative cognitions related to dowries.
References
<references>
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/society/dowry/dowry-system-in-india-problems-social-dimensions-and-other-details/35175/
- ↑ https://www.lawctopus.com/academike/dowry-poverty/
- ↑ Buhler, G. (1964). The laws of Manu (Vol. 25). New Delhi, India: Motilal Banarsidass.
- ↑ https://www.quora.com/When-and-how-did-the-dowry-system-start-in-India
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 http://www.gurbani.org/articles/webart69.htm
- ↑ http://www.islamswomen.com/marriage/fiqh_of_marriage_6.php
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 http://www.islamawareness.net/Marriage/Dowry/dowry_article001.html
- ↑ http://paa2010.princeton.edu/papers/100225
- ↑ Agnihotri, I. (2003). The expanding dimensions of dowry. Indian Journal of Gender Studies, 10, 307–319. doi:10.1177/09715215- 0301000206
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 http://vijayendrarao.org/papers/dowryecon.pdf
- ↑ Banerjee, P. R. (2014). Dowry in 21st-century india: The sociocultural face of exploitation. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 15(1), 34-40. doi:10.1177/1524838013496334
- ↑ http://lawcommissionofindia.nic.in/1-50/report42.pdf
- ↑ http://www.vakilno1.com/bareacts/dowryprohibitionact/dowryprohibitionact.html
- ↑ http://nyaaya.in/law/557/the-protection-of-women-from-domestic-violence-act-2005/
- ↑ http://users.skynet.be/fa103362/indiahuis/Home/Dowry/ISADABBI/isadabbi.html
- ↑ http://www.humanityfoundationindia.org
- ↑ http://www.comminit.com/global/content/fight-against-dowry
- ↑ http://www.agniraksha.org
- ↑ https://www.facebook.com/nodowryclub/