Course:EDCP371 951 2010/Cooperative learning
Post your quote from the text, research, images, videos, and diagrams here!
Quotes
- non-example In conversations about these topics, the reason we fail to reach more constructive outcomes can be understood partly in terms of a very significant lack: the lack of a sophisticated and shared understanding of how to approach questions of technology
- Neo-Luddism has become something of a contemporary rallying cry for a number of individuals and groups engaged in analyzing and/or resisting technology in some form or another
- technologies of the world become a means of carrying out human will. However technologies are extensions of our perceptions and abilities, then changing our technologies changes how humans perceive and interact with the world; in many ways this changes humans themselves (page 52)
- medium is the message (Marshall McLuhan)
Shab's
Alison's
Chelsea's
Peter O.
“Major technological decisions become mere technical matters that do not demand or justify the consultation of nonexperts. Consequently, the technological progress story has been used to promote more authoritarian and technocratic decision making and to suppress democratic decision making.” -Slack and Wise, p.23
Slack and Wise highlight the importance for group discussion. It is a powerful practice used by business and the cooperation involved is a good skill to practice and gain in school.
Groups:
•Informal/formal
•Team or party
Group environment components: •Creativity •Responsibilities •Constructive feedback •Conflict resolution skills •Problem solving skills (Petrina, p.107, 2007)
Joe's Take
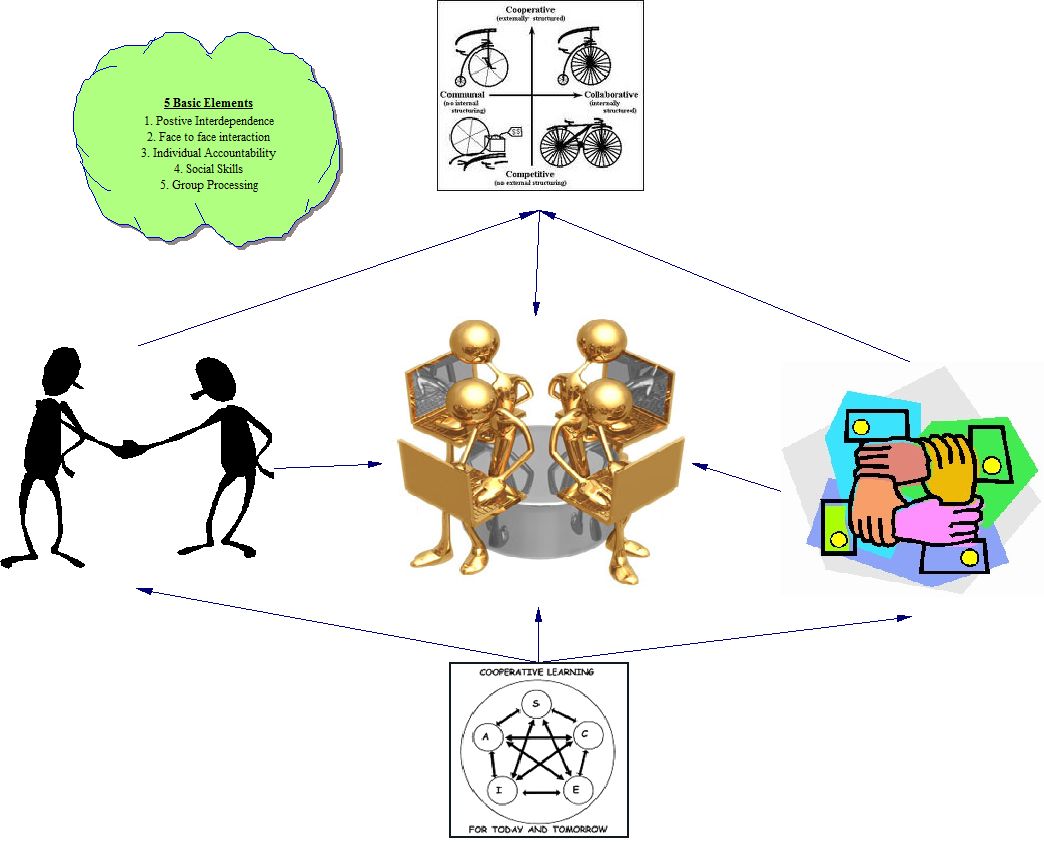
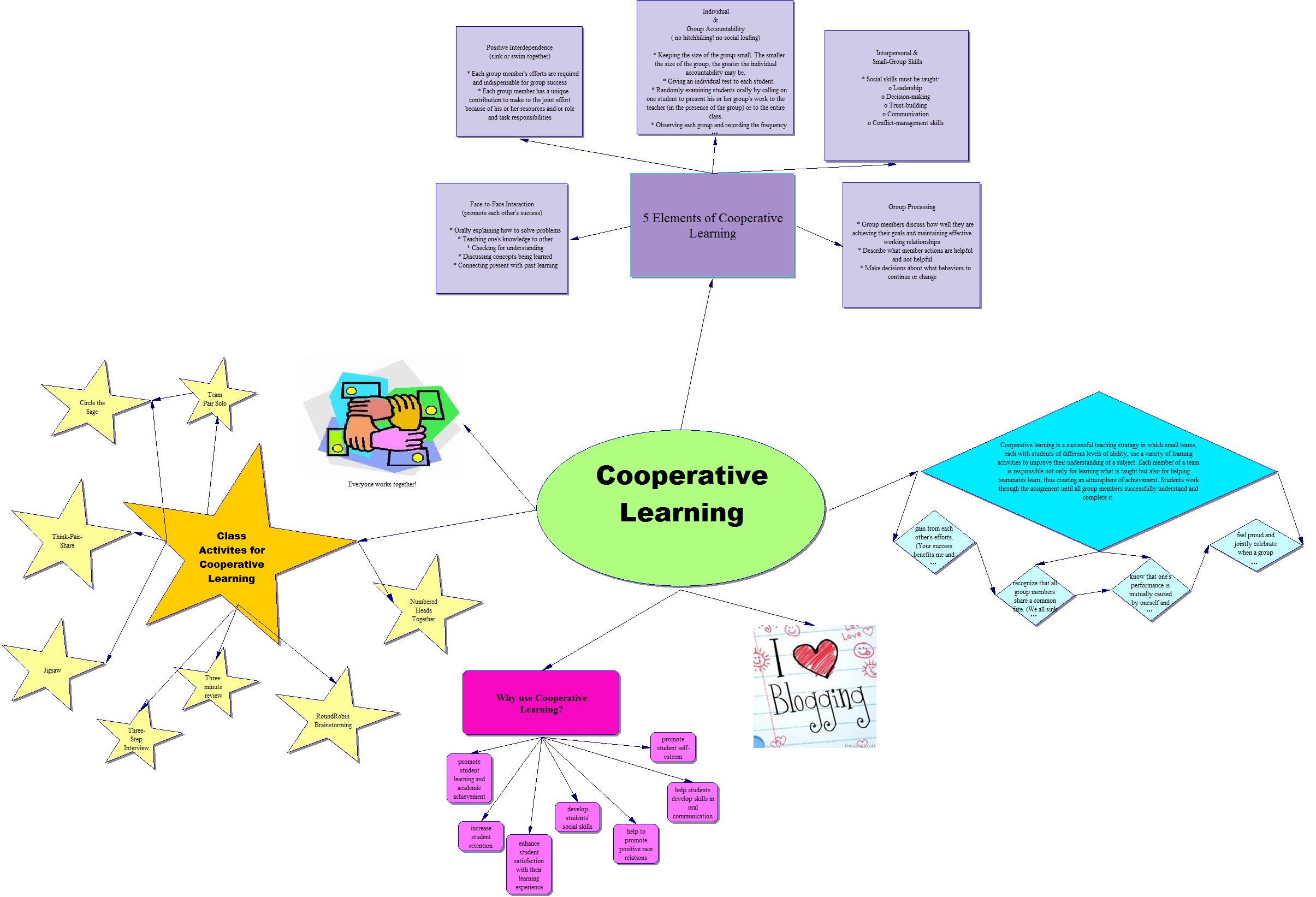
Cooperative learning is a successful teaching strategy in which small teams, each with students of different levels of ability, use a variety of learning activities to improve their understanding of a subject. Each member of a team is responsible not only for learning what is taught but also for helping teammates learn, thus creating an atmosphere of achievement. Students work through the assignment until all group members successfully understand and complete it. [1]
- Cooperative efforts result in participants striving for mutual benefit so that all group members:
- gain from each other's efforts. (Your success benefits me and my success benefits you.)
- recognize that all group members share a common fate. (We all sink or swim together here.)
- know that one's performance is mutually caused by oneself and one's team members. (We can not do it without you.)
- feel proud and jointly celebrate when a group member is recognized for achievement. (We all congratulate you on your accomplishment!).