Course:SPPH381B/Essay 2/Vulnerable Workers - Ye-Von Lee
There are endless types of hazards and risks that exist in majority of workplaces. However, some groups of workers are more vulnerable to workplace related diseases and injuries [1]. Vulnerable workers can be defined as workers who have greater exposure to risks of injuries and illnesses or suffer disproportionately when injured such as immigrants, due to a variety of reasons [2]. As a result, their health and safety on the job are at much greater risk than those who work in firms that ensure the safety and wellness of their employees strictly [1]. It should be a right for all workers to have protections for their health, safety and wellbeing, however due to the nature of certain workplaces, this is not the case. The label vulnerable worker applies to many different groups of people [2]. There are factors influencing the risk of being a vulnerable worker. It can be a simple reason of just being who you are, your socioeconomic status or your work environment [3].
Personal Factors
Age
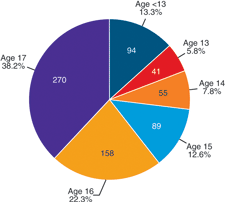
Youth workers are at risk of being vulnerable workers. The reason for this is because they are likely to be reluctant to identify and alert their employers about the dangerous that exist in the workplace due to the fear of losing their jobs [4]. Also, it is difficult for them to effectively identify and control hazards because of their inexperience and knowledge about the workplace [4]. These include retail outlets [4]. Unfortunately, the majority of workers working in these environments are young workers. Youth workers range from the age of 14-22. As a result, they lack the experience and education to obtain a traditional workplace environment occupation. Additionally, most youth workers are new to the job. It has been shown in research, that many workplace injuries occur in the first month of the job [1]. As a result, it is important for young workers themselves and parents, teachers and employers of the workers to make sure that the young workers safety is ensured on the job. For example, parents can help identify hazards and risks for the young worker or provide insight and knowledge about the workplace based on their personal experiences [1].
Gender
Similar to young workers, female workers are prone to more risks at the workplace because they may be more reluctant to stand up for themselves or let their employers aware of certain hazards. Also, there are higher risks of sexual harassment for women, which can happen in the workplace compared to men.
Education and Income
Higher education heightens the probability of obtaining a unionized, high paying and safety ensuring occupation in comparison to not having higher-level education. As a result, those who do not have recognized education or experience, will be more prone to obtain non-unionized which are more likely to not have the sufficient care and protection for the workers. Also low-income workers deal with more difficulties in ergonomics and safety in comparison to high-income workers. For example, low income workers engage in work that is more often repetitive in motion, overexerts their body, and requires lifting [5]. Also, they are more often at of risk of falls, slips, cuts, burns, collisions and entrapments [5].
Socioeconomic Status
Precarious employment (including part-time, temporary, seasonal workers)
Precarious workers are those who have jobs with low wages, no pensions, no union and small firm size [6]. These can include temporary foreign labor, service industry jobs, food services and accommodation jobs or self-employment [6]. Precarious work has significant effects of people physically and mentally [6]. Workers who engage in precarious work are more likely to struggle with job insecurity, the pressure of holding more than one job, irregular or long hours, lack of legal protections and insecure visa status [6]. Additionally, these workers are in risk of health consequences because they have low income and protection in comparison to the work they actually partake in [6]. For example, they may not be able to book off days due to income when they need to rest. Another issue is that these workers are very unlikely to get opportunities to upgrade their skills and status to move on to better and higher wage work [6]. Furthermore, due to the insecurity of their employment, precarious workers are at risk of financial insecurities and poverty. This can lead to mental deteriorations caused by chronic stress. As a result, they are forced to remain in the same workplace for long periods of time, which eventually leads to long-lasting effects on their health.
Immigrants/ Refugee or Temporary Foreign Labor Workers
Immigrants, refugee status or temporary foreign labor workers engage in the most precarious work occupations. Also, they will not complain to their employers in the fear of losing their jobs. Their work is highly physically demanding and dangerous which causes them to have higher rates of accidents [1]. Risks are induced by the lack of experience or training, lack of knowledge about health and safety rights and fear of losing the job or possibly being deported [6]. Additionally, most of these workers may not have appropriate documentation that allows them to receive the rights [2]. As a result, they have many barriers that block them from receiving the legal protections [6]. Furthermore, communication barriers are another factor that limits these workers safety. Many of these workers do not have adequate English language skills [2]. This can cause miscommunications between the employer and employee regarding their rights, safety and risks.
Work Environment
Ununionized work place
Non-unionized work places lack the benefits and have lower wages in compared to unionized occupations [6]. Unionized jobs offer their employees with health benefits, which can include prescription drugs, vision and dental coverage that can ensure the health of their employees further. Furthermore, unions provide workers with support and a voice that allows them to speak up about possible problems in the workplace. As a result, issues and complications of the workplace are more quickly resolved with the help of a union. Additionally, unionized occupations offer more training opportunities, which can lead to possible salary raises or promotions.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Government of Canada, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. "Vulnerable Workers | Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety." Government of Canada, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. N.p., 06 Oct. 2016. Web. 03 Mar. 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Vulnerable Workers." Public Services Health and Safety Association. N.p., n.d. Web. 03 Mar. 2017.
- ↑ Lecture 10
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Foster, J. and Barnetson, B. (forthcoming). Dead today, gone tomorrow: The framing of workplace injury in Canadian newspapers, 2009-2014. Canadian Journal of Communications.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lecture 4
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Mckay-Panos, Linda. "Issues Faced by Vulnerable Workers in Canada." LawNow Magazine. N.p., 15 Sept. 2016. Web. 03 Mar. 2017