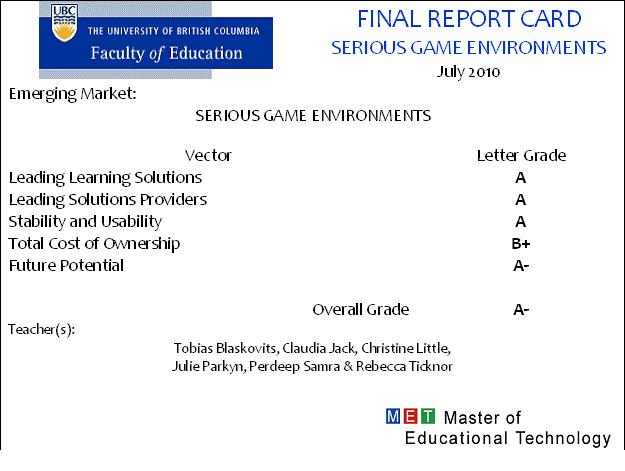
Course:ETEC522/2010ST1/SeriousGameEnvironments/ReportCard
Final Vector Analysis
Discussion Questions
All comments and/or responses to the discussion questions were posted to the ETEC 522 WordPress Blog.
Here is a summary of the responses and comments to the discussion questions pertaining to each vector. In addition we have provided a reflection question that might guide us towards improving this Open Educational Resource (OER) for future participants.
Vector 1
After experiencing what it is like to interact in a virtual simulation like Second Life, comment on a few of the benefits and drawbacks of using this type of technology to facilitate learning.
Approximately eighteen people were able to join the Second Life tour held one evening. Schedules and technical issues prevented others from joining who wanted to. Thanks to everyone who provided feedback. Following is a summary of the benefits and drawbacks mentioned surrounding use of this type of technology for learning.
Benefits
- Many simulations can be generated in a virtual environment; some of these simulations would be impossible/very difficult in real life (e.g. stock market simulations, life/death medical situations, war games).
- Training can be done virtually on systems that cost too much to purchase for education (e.g. $10m medical equipment is too costly, yet it can be virtualized and students can interact with it online).
- Access is anywhere, anytime from a myriad of devices.
- It provides a virtual experience that more closely mirrors face-to-face due to the fact that avatars are face-to-face.
- It offers a sense of exploration and experimentation that appeals to many.
- Fosters an ability to interact with people all over the world to develop global views and experience different perspectives.
- Can style virtual environment to appeal to learners and make them comfortable (we offer seating for avatars, but do they really need to sit? They will never get tired standing.
- It enhances distance learning by bringing students together in a ‘community.’
- Students may access outside of school hours, extending their learning.
Drawbacks
- Gaming can be addictive/distracting – this resonated with several people who felt that certain personalities might lose focus of the goal or become addicted.
- Lots of ProD necessary to get comfortable with the environment.
- Program requirements limit access to newer computers in schools only due to graphics and processing power.
- Content and language may not be appropriate – in this case, we would need to limit student access to private islands/areas that are off-limits to the general public.
- May not be appropriate for elementary panel or where students are already physically together.
- Careful planning necessary to make material relevant, and technical support a necessity as teachers don’t have time to manage issues that may arise.
Summary
Virtual environments such as Second Life may play a key role in offering a engaging learning atmosphere that allows for exploration and experimentation. Virtualized training can be very effective, particularly when it is not feasible in real life. Concerns about content creation, technology issues and loss of focus must be considered when developing this environment for education. This type of environment might be considered for teenagers and older.
Vector 2
Compare and contrast the strengths and weaknesses of free and "pay to play" educational games.
The discussion on the WordPress site regarding “pay to play” and free educational games yielded many interesting responses. Most respondents chose to compare the two educational game groups by identifying the advantages and disadvantages present in "pay to play" and free games.
"Pay to Play" Games
Advantages:
Many felt that "pay to play" games have three main advantages over their free counterparts. Firstly, the overall quality of "pay to play" games was better than free games. These games typically contain better graphics and more intriguing tasks to complete. Secondly, many stated that "pay to play" games were more stable. If a teacher wants to purchase a game for the classroom they will own the copy and not have to worry about losing access to the game if the free website removes the link to the game. Thirdly, "pay to play" games contain fewer distractions such as pop up ads. This allows the player to focus on the game rather than being over whelmed by everything else on the screen.
Disadvantages:
Two main disadvantages emerged on the discussion board. The first disadvantage was the higher cost associated with playing a game that is not free. Players would have to buy the game and buy a console or computer to play the game on. The second disadvantage is the fact that very few "pay to play" games offer free trials. This means that one might invest in a game that may end up being less effective than the purchaser had originally anticipated.
Free Games
Advantages:
The main advantage free games have is that the games can be played free of charge. Free games are also more accessible to schools as they tend to already have computers. Therefore, downloading free games add no additional expenses. Lastly, free games may be easier to use for individuals that are not familiar with games as they tend to have much more straight forward and basic concepts.
Disadvantages:
Numerous disadvantages regarding free games continuously surfaced on the discussion board. Firstly, free games tend to have a lower overall quality (when compared to “pay to play” games). For example, the concepts and graphics tend to be simplistic. Secondly, downloading free games may cause the computer to crash or slow the computer’s performance. Thirdly, free games are not overly stable as they can disappear off the Internet at any time. Lastly, pop up ads and other types of advertisements can make it difficult for younger students to simply play the game as they may become distracted.
Vector 3
Provide an example of a serious game that you have used in the classroom or for professional or personal development. Comment on usability of the game based on the ten dimensions of effective serious games, as discussed in this vector.
An analysis of the responses to Vector 3 revealed that many participants have never really been serious gamers and some have never used video games nor web based games in their teaching. A few have experimented with content related games such as Mathblaster and chemistry games, however, many have confessed to recognizing the benefits of using serious games in their lessons. Most have been using games for personal and intellectual development, stress relievers, and just for fun. These include Empire Total War, Star Wars, SimCity, and various Nintendo games which could also be used to teach educational content, as well as Wii sport games and other entertainment games. The games designed for training and entertainment were given higher ratings on the ten dimensions than those designed for education.
Some of the general positives include usability features such as:
- Consistent responses to the user’s actions.
- Good realistic images
- Multilevel challenges
- The realistic actions
- Provision for learners to skip levels
- Built in guidelines for users to familiarize themselves with and master the game
- Customization opportunities.
- Provision of feedback on progress resulting in high levels of interest and motivation.
The few educational games suggested did not rate as highly on the 10 dimensions and a few of the dimensions were not observed in some of the games. For example they did not allow users to skip non-playable and frequently repeated content nor allow users to customize video and audio settings, difficulty and game speed. The main concern was that they could be boring, lacked the quality graphics found in commercial games and the level of freedom users would have to customize.
For most people, their exposure to Second Life was interesting and allowed them to see the possibilities of integrating it in their teaching. They have commented favourably on its usability features as well.
The information on gaming has provided a new dimension to their thoughts on teaching strategies and has revealed a whole new world for them to explore.
Most participants felt there was a future for serious games and indicated a willingness to employ these in future classroom practices.
Vector 4
If you were in the position of purchasing serious games for your school or business, which of type gaming system would you choose, a computer-based system or console-based system? Why? Base your argument on the total cost of ownership alone.
In an era of shrinking school budgets, the discussion surrounding the total cost of ownership of systems capable of running serious games was one which was heated. The responses to this question were nearly split down the middle, with 57% of respondents choosing to purchase a computer-based system, and 43% choosing to purchase a console-based system.
Proponents of the computer-based systems generally saw costs associated with serious games as prohibitive. As a result, they cited the existing infrastructure concerning computers, networks and maintenance issues in schools, and the interchangeability/upgrading of computer components as the main reasons behind their choice.
Proponents of console-based systems argued that consoles allowed more students to participate with a single system than with a single computer system at any given time. They also cited the fixed costs of the systems, the number of games available, and the longer shelf life of the system compared to that of a computer, as the main reasons behind their choice.
Some other issues emerged during the discussion, including the notion of handheld gaming systems vs. computer and console-based systems, the idea of gaming systems being perceived as a waste of money by tax payers, and whether or not major gaming companies such as Sony, Microsoft or Nintendo were joining the serious games initiative.
Vector 5
How can serious games accomplish and reach some of the discussed goals that will drive education in the future?
There has been much agreement in discussion that serious games can be used to heighten student interest, engagement and excitement about learning and that serious games could certainly be used as an additional teaching tool. However, it remains challenging to incorporate the engaging and appealing nature of commercial games with the potential for intellectual and social growth. There is the need for greater instructional design into serious games for use in the classroom while still retaining engagement and appeal to students. Game developers must be encouraged to find the best way to bring educational value to fun games.
Participants recognized that many serious games currently offer opportunities to exercise critical thinking and decision making skills, for self direction of learning and for participation in communities of practice, allowing learners to be active participants in the learning process. Serious games may allow students to learn increasingly through experimentation providing venues to make mistakes and learn by correcting them. It is important for games to incorporate content while providing valuable opportunities for self-reflection and feedback response to actions. Students should have a sense of personal involvement and feel that they are part of a shared experience among other students. It was also suggested that there should be a role that the instructor can play within the serious gaming environment such that he or she could act as a guide who could provide connections to future and past material and ensure students are navigating effectively.
After participation in our Second Life experience, it became evident to some how role play and simulations within serious games provide increased authenticity to tasks. Budgetary and time constraints of institutions may provide greater opportunity for simulation type games which can provide authentic experiences; such as visiting other places, using expensive equipment, collaborating and interacting with other students in different geographic locales.
It was also suggested that serious games offer potential for the subliminal acquisition of knowledge. It is important for teachers however to ensure knowledge is accurate or exploit opportunities of inaccuracy as teachable moments to clarify misrepresentations. The high interest inspired by games may also result in further exploration of topics outside of the gaming environment.
Incorporating serious gaming into lessons allows teachers to design more creative, innovative and engaging learning opportunities. Instructors must not only see value in the gaming experience, they also must fully consider exactly how gaming will be incorporated to ensure educational value and the accomplishment of learning objectives. Within discussions, it became evident that teachers must clearly identify objectives and goals for student participation in gaming before implementation can occur. It was also suggested that games may do a better job at stimulating students than traditional instruction prompting responses indicating that it may be effective to design lessons around particular games.
Music, interactivity, immediate feedback, high quality graphics, intrinsic motivation, challenge, rewards, consequences and self-pace affordance contribute to the stimulating nature of games and it may be useful to draw upon these components in lesson design.
Participants also indicated that perhaps serious games may offer opportunity for integrating multiple subject areas and learning objectives in one learning experience, a task many teachers struggle with on an ongoing basis. Serious games would also allow students different avenues to demonstrate understanding, an excellent opportunity for differentiated learning.
Further, some recognized a value in having students take a role in game development, allowing games to become truly open source such that they can me modified and built upon by subsequent users; perhaps a very valuable collaborative learning experience for students.
Some concerns arose however surrounding using serious games to accomplish future goals of educations. In regards to assessment, it will be important to build in elements for assessment to ensure students are grasping objectives. With or without serious games, it became important to recognize that teachers must reflect upon their practice such that they are providing engaging learning opportunities for students and to make changes to practices that are not effective. Reflective practice is essential and it is important to consider that serious games may not be a “solve-all” in the classroom.
Participants also recognized that incorporating games in the classroom has considerations that must be weighed. It is essential to make sure the game offers enough content to ensure effective learning while at the same time not be boring. Time devoted to game play must translate to the efficient accomplishment of learning objectives.
Reflection
As an EVA, comment on whether you believe that the serious games market would be one you might invest in. Does it have more appeal as an investor than the previous technologies that have been reviewed in this course so far (social, mobile, open source, 1:1, collaboration, etc.)?
Upon careful reflection, many individuals feel that serious game environments are an emerging market that should definitely attract attention from investors. Those that support serious game environments cite the attractive benefits of serious games. Serious games play a valuable role in providing an alternate venue for educating those with special needs. Games are interactive and social in nature, allowing for collaboration and the building of learning communities. Some serious games include open source code which allows users to manipulate and enhance the selected games towards their purposes. Serious games promote constructivist ideals such as problem solving, knowledge building, and learning through failure. Games are entertaining, creating an environment where users are engaged, immersed in content, and provide opportunities for tangential learning. Serious games also seem to work well with other emerging markets such as one-to-one learning, collaboration, and mobile technologies.
Those that choose to support serious games caution the audience in which this type of technology would be administered. Cost was seen as a major factor, and many felt that serious games might not be as feasible in the public education sector. Most people agreed that serious games provide many benefits for business and higher education settings, which can afford to pay for specifically designed games, for the purpose of training, simulations, distance education, and alternatives to f2f classrooms. Like the other emerging technologies, serious game environments must suit the needs, affordability, and access of the intended target audience.
While most see the potential in serious game environments, there are still many questions involving the logistics of incorporating them into the traditional learning environment. Concerns centered around the addictive nature of gaming and the costs associated with building game environments into our education system. Other concerns were about lack of sensitivity to certain cultural, moral and ethical issues. If these issues were addressed or easily controlled from administrative standpoint, then even those hesitant to invest in serious game environments would be supportive of such technological innovation.
Conclusion
Thank you for taking the time to complete our emerging market analysis on Serious Game Environments.
We look forward to your comments and feedback.